Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
In Kubernetes, StatefulSets are used to run stateful applications that require stable storage, ordered deployment, and persistent identities.
In this guide, we manually create a PersistentVolume (PV) using hostPath, then deploy a StatefulSet that uses this PV for data persistence. In Kubernetes, some applications need to store data permanently and keep their names stable even if pods restart.
StatefulSets are designed to manage these stateful applications.
Prerequisites
-
- A Kubernetes cluster (Vagrant/Kubeadm/Minikube)
-
- At least one worker node
-
kubectlconfigured on the master
-
- Worker node must allow port 10250
Create StatefulSet (1 replica)
Command:
nano nginx-statefulset.yamlPaste this,
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "web"
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.25
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
volumeName: nginx-pv-0Explanation:
-
- Opens/creates a file named nginx-statefulset.yaml.
-
- This file contains the YAML configuration for your StatefulSet.
Expected Output:

2.Command:
kubectl apply -f nginx-statefulset.yamlExplanation:
-
- Deploys StatefulSet with 1 pod.
-
- Auto-creates PVC
www-web-0.
- Auto-creates PVC
-
- Binds PVC to the PV you created.
Expected Output:

Verification
1.Command:
kubectl get pvExplanation:
Shows status of all PVs.
Expected Output:

2.Command:
kubectl get pvcExplanation:
-
- Shows PersistentVolumeClaims.
-
- PVC should be Bound
Expected Output:

3.Command
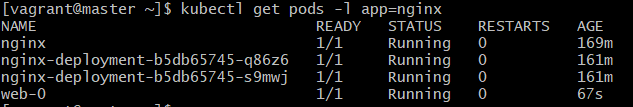
kubectl get pods -l app=nginxExplanation:
Lists all pods with label app=nginx.
Expected Output:
Test Data Persistence
Command:
kubectl exec -it web-0 -- /bin/bashExplanation:
-
- Opens terminal inside the pod.
Expected Output:

Command:
echo "Hello StatefulSet" > /usr/share/nginx/html/test.html exitExplanation:
Writes test data into mounted volume.
Expected Output:
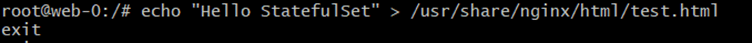
Verify again:
Command:
kubectl exec -it web-0 -- cat /usr/share/nginx/html/test.htmlExplanation:
Reads the file to confirm data is stored.
Expected Output:
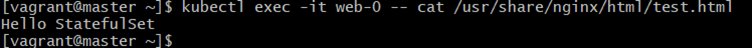
Delete pod:
Command:
kubectl delete pod web-0Explanation:
-
- Deletes the pod manually.
-
- StatefulSet will recreate it automatically
Expected Output:

When pod restarts
Command:
kubectl exec -it web-0 -- cat /usr/share/nginx/html/test.htmlExplanation:
Checks if file still exists → confirms persistence.
Expected Output:
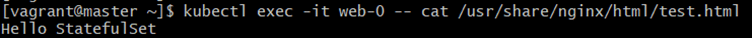
conclusion
Deploying a StatefulSet with a manually created PersistentVolume using hostPath demonstrates how Kubernetes handles stateful workloads at a low level. By creating the PV, headless service, and StatefulSet step-by-step, we clearly see how stable identities, persistent storage, and ordered pod management work together. This setup ensures that each pod receives dedicated storage and retains data across restarts, providing strong reliability for stateful applications. Although manual PV creation is mainly suited for learning environments, it builds a solid foundation for understanding storage behavior before moving to dynamic provisioning in production.
For more information about kubernetes you can refer to jeevi’s page





