Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
In modern cloud-native environments, organizations are increasingly adopting Kubernetes to deploy and manage applications. While Kubernetes provides powerful primitives such as Pods, Services, and Deployments, it also introduces significant complexity. Developers are often required to understand low-level infrastructure concepts, YAML configurations, and operational details that are outside their core responsibility.
KubeVela was created to solve this problem by simplifying application delivery on Kubernetes. It provides a higher-level, application-centric platform that allows developers to focus on what to deploy, while operators define how it should be deployed.
What is KubeVela?
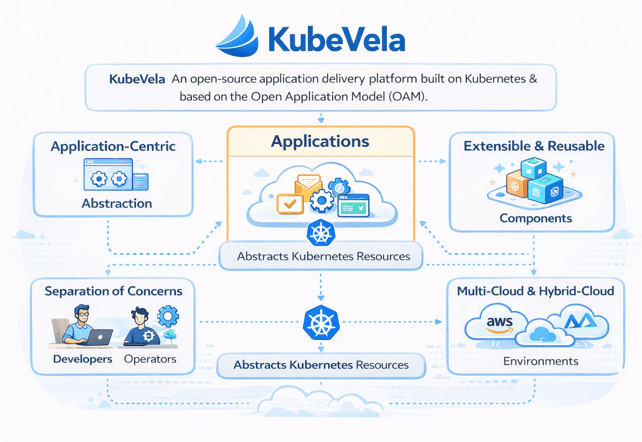
KubeVela is an open-source, modern application delivery platform built on top of Kubernetes and based on the Open Application Model (OAM). It abstracts Kubernetes resources and provides a consistent way to define, deploy, and operate applications across different environments.
With KubeVela, an application is treated as a first-class object rather than a collection of Kubernetes resources. This approach improves clarity, reusability, and operational efficiency.
Key characteristics of KubeVela include:
- Application-centric abstraction
- Separation of concerns between developers and operators
- Extensibility through reusable components and traits
- Multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud support
Why KubeVela is Needed ?
Although Kubernetes is powerful, it is not developer-friendly by default. Developers often face challenges such as:
- Writing and maintaining large YAML files
- Understanding infrastructure-specific configurations
- Managing application lifecycle across environments
- Handling scaling, rollout, and policy enforcement manually
KubeVela addresses these challenges by providing opinionated abstractions and reusable building blocks. It enables platform teams to define standards, while allowing application teams to deploy faster with fewer errors.
Core Concepts of KubeVela
Understanding KubeVela becomes easier when its core concepts are clearly explained.
1.Application
An Application in KubeVela represents the complete definition of a deployable system. It includes components, policies, and workflow steps. This single object defines what the application is and how it should behave throughout its lifecycle.
2.Components
A Component defines a workload type, such as a web service, worker, or database. Internally, components map to Kubernetes resources like Deployments or StatefulSets, but developers do not need to manage those details.
3.Traits
A Trait adds operational behavior to a component, such as:
- Autoscaling
- Ingress exposure
- Resource limits
- Health checks
Traits allow operational concerns to be attached without modifying the core application logic.
4.Policy
A Policy defines rules and constraints for application deployment, such as:
- Placement policies (region, cluster)
- Security and compliance rules
- Environment-specific configurations
5.Workflow
A Workflow defines the deployment process, including steps like:
- Deploy to staging
- Run tests
- Manual approval
- Promote to production
This enables GitOps-style and CI/CD-driven application delivery.
Developer vs Operator Responsibilities
One of the most important benefits of KubeVela is the clear separation of responsibilities.
Developers
- Define application components
- Configure high-level traits
- Focus on business logic
Operators / Platform Engineers
- Define components and traits
- Enforce policies and standards
- Manage infrastructure and security
This separation improves collaboration, governance, and platform scalability.
Key Benefits of Using KubeVela
KubeVela provides several strategic advantages:
- Reduced Complexity: Abstracts Kubernetes internals
- Consistency: Standardized application delivery across teams
- Extensibility: Custom components and traits
- Portability: Works across clouds and clusters
- Improved Productivity: Faster onboarding and deployment
These benefits make KubeVela especially suitable for organizations building internal developer platforms.
Common Use Cases
KubeVela is widely used for:
- Internal Developer Platforms (IDP)
- Microservices application delivery
- Multi-cluster and multi-cloud deployments
- Standardized CI/CD workflows
- Enterprise governance and compliance
Security and Governance in KubeVela
Security and governance are core design considerations in KubeVela. Through policies and platform-defined rules, organizations can enforce security standards without requiring developers to manage them manually.
Key security capabilities include:
- Policy-driven access control
- Environment-based restrictions
- Controlled exposure of services
- Separation between application definition and infrastructure privileges
This model helps enterprises maintain compliance while preserving developer autonomy.
Observability and Operations
KubeVela integrates well with observability and operational tooling in the Kubernetes ecosystem. Platform teams can standardize logging, monitoring, and alerting behaviors through reusable traits and policies.
Operational benefits include:
- Consistent observability across applications
- Reduced operational overhead
- Easier troubleshooting through standardized patterns
KubeVela CLI and Developer Experience
The KubeVela CLI (vela) provides a simplified interface for interacting with applications and environments. It abstracts complex Kubernetes commands and offers a more intuitive workflow for developers.
With the CLI, teams can:
- Initialize applications
- Manage components and traits
- Monitor application status
Challenges and Limitations of KubeVela
While KubeVela provides significant advantages, it is important to understand its limitations, especially for beginners and organizations planning adoption.
Some common challenges include:
- Learning Curve: Although simpler than raw Kubernetes, KubeVela still requires basic Kubernetes knowledge.
- Ecosystem Maturity: Compared to Kubernetes, the ecosystem and community are smaller.
- Customization Effort: Defining custom components and traits requires platform engineering expertise.
- Debugging Complexity: Abstracted layers can make troubleshooting harder for new users.
Understanding these challenges helps teams adopt KubeVela realistically and plan proper training and platform support.
When Should You Use KubeVela?
KubeVela is not mandatory for every Kubernetes setup. It is most effective in the following scenarios:
- Organizations managing multiple teams and microservices
- Companies building an Internal Developer Platform (IDP)
- Environments requiring strong governance and policy enforcement
- Multi-cluster or multi-cloud deployments
- Teams aiming to standardize CI/CD and application delivery
For small or experimental projects, plain Kubernetes may be sufficient. For scalable and enterprise-grade platforms, KubeVela provides long-term value.
KubeVela and Internal Developer Platforms (IDP)
KubeVela plays a critical role in building Internal Developer Platforms. It acts as the application delivery engine that sits between developers and Kubernetes infrastructure.
By integrating KubeVela with CI/CD tools, source control, and observability systems, organizations can create a self-service platform that improves productivity and consistency.
Key IDP capabilities enabled by KubeVela include:
- Self-service application deployment
- Standardized environments
- Built-in policies and guardrails
KubeVela in Real-World Enterprise Environments
In real-world enterprises, KubeVela is often used as part of a platform engineering strategy. Platform teams define reusable components, traits, and policies, while application teams consume them through simple application definitions.
This approach enables:
- Faster onboarding of new developers
- Reduced operational errors
- Strong governance without blocking developer velocity
- Alignment with DevOps and GitOps practices
KubeVela Architecture Overview
KubeVela operates as a control plane on top of Kubernetes. It uses Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to manage applications and controllers to reconcile desired state with actual state.
At a high level, the architecture consists of:
- KubeVela CLI (vela)
- Application Controller
- OAM-based CRDs
- Kubernetes cluster as the runtime environment
This design ensures that KubeVela integrates seamlessly with existing Kubernetes tooling while adding powerful abstractions.
Conclusion
KubeVela represents a significant step forward in simplifying Kubernetes application delivery through an application-centric and platform-driven approach. By abstracting infrastructure complexity and standardizing deployment patterns, it enables developers to focus on delivering business value while allowing platform teams to enforce governance, security, and operational best practices.
KubeVela offers a structured and less overwhelming entry point into the Kubernetes ecosystem. It introduces core platform engineering concepts such as separation of concerns, reusable abstractions, and policy-driven operations in a practical and approachable manner. As experience grows, the same platform can scale to meet enterprise-grade requirements without fundamental redesign.
In modern cloud-native environments where consistency, scalability, and developer productivity are critical, KubeVela stands out as a reliable application delivery framework. Whether used for learning, internal developer platforms, or large-scale enterprise systems, KubeVela provides a strong foundation for building and operating Kubernetes-based applications with confidence and control.





