Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Cloud Computing ?
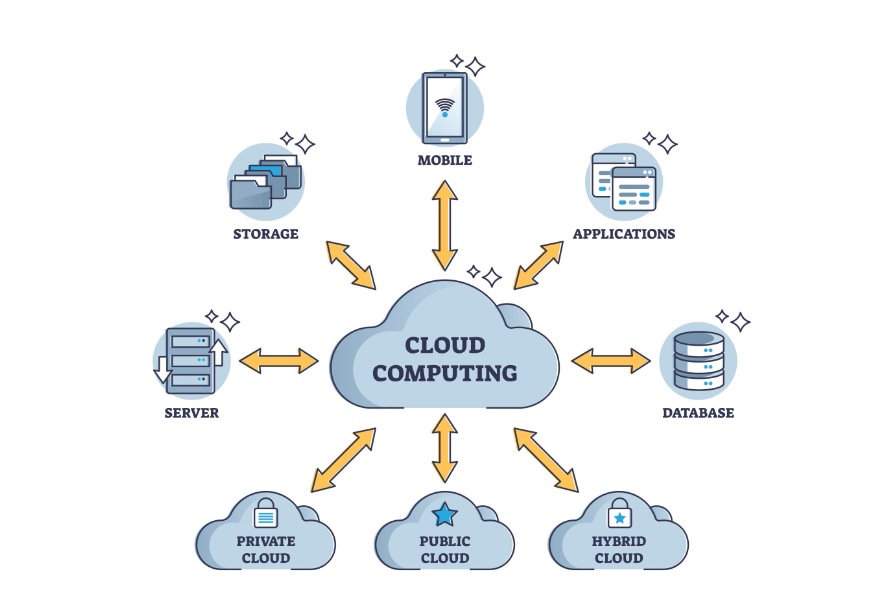
In simple terms, Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the Internet (“the cloud”).
Instead of keeping files on a local hard drive or managing physical servers in an office, you access these resources from providers like Amazon (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), or Google (GCP).
How It Works: The “Rental” Model
Think of cloud computing like a utility company. Just as you don’t build a private power plant to turn on your lights, you don’t build a private data center to run an app. You plug into the grid and pay only for the electricity (or computing power) you use.
Phase 1: Linux & Scripting Foundations
Linux Introduction: Learning the open-source operating system that powers over 90% of the world’s cloud infrastructure.
File & Directory Management: Mastering the CLI (Command Line Interface) to navigate, create, and organize the Linux file system.
User/Group Management & Permissions: Controlling who can read, write, or execute files to ensure system security.
Sudo vs Su: Understanding the difference between switching to the root user (su) and executing commands with elevated privileges (sudo).
Links (Hard vs Soft): Managing file shortcuts; “Soft” links are like Windows shortcuts, while “Hard” links point directly to the data on the disk.
Package Managers: Using tools like yum or apt to install, update, and remove software automatically.
Standard I/O & Source Command: Mastering data flow (input/output) and executing scripts in the current shell environment.
Shell Scripting: Writing Bash scripts to automate repetitive tasks using variables, loops, and scheduled “cron jobs.”
Git & GitHub Basics: Learning Version Control Systems (VCS) to track code changes and collaborate with teams.
Phase 2: Networking & Security
OSI & TCP/IP Models: Understanding the theoretical and practical layers of how data travels across a network.
IP Addressing & Subnetting: Learning how to identify devices and divide large networks into smaller, manageable segments.
Ports & Protocols: Identifying communication channels (like Port 80 for HTTP) and the rules (protocols) they follow.
Ping, TCP Handshake, & NIC: Testing connectivity and understanding how devices establish a stable “handshake” connection.
Firewall, Proxy, & DNS: Managing traffic filters, intermediate servers, and the “phonebook of the internet” (DNS).
SSL/TLS & mTLS: Securing data in transit through encryption and mutual authentication between services.
Cloudflare Fundamentals: Learning how Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) protect and speed up websites globally.
Phase 3: Cloud Concepts & Service Models
Real-life Examples: Connecting theory to daily apps like Netflix (streaming) and WhatsApp (backups) that run on the cloud.
Core Benefits: Understanding why businesses switch to the cloud for cost savings, global reach, and “High Availability” (uptime).
Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS): Differentiating between renting raw hardware (IaaS), platforms for coding (PaaS), or finished software (SaaS).
Scalability & Elasticity: Learning how the cloud grows to meet demand (Scalability) and shrinks back to save money (Elasticity).

Phase 4: AWS Core Services (Compute, Storage, Database)
AWS Compute (EC2): Creating and managing virtual servers in the Amazon cloud with custom CPU and RAM.
Auto Scaling & Load Balancing: Automatically adding servers during traffic spikes and distributing traffic evenly among them.
AWS Storage (S3, EBS, EFS): Choosing between object storage (S3), virtual hard drives (EBS), or shared file systems (EFS).
Snow Family & Storage Gateway: Moving massive amounts of physical data into the cloud using rugged hardware devices.
AWS Databases: Managing structured data (RDS/Aurora), NoSQL data (DynamoDB), and high-speed caching (ElastiCache).
Analytics Tools: Using services like Redshift for data warehousing and QuickSight for visual business reports.
Phase 5: AWS Advanced Networking & Security
VPC & Subnets: Building your own private, isolated section of the AWS cloud to host your resources.
Security Groups vs NACLs: Setting up “firewalls” at the instance level (Security Groups) and the subnet level (NACLs).
IAM (Identity & Access Management): The most critical service for managing users and their specific permissions to AWS resources.
Encryption (KMS & ACM): Managing digital keys and SSL certificates to keep sensitive data unreadable to hackers.
Monitoring (GuardDuty, Inspector): Using AI-driven tools to detect threats and vulnerabilities in your cloud environment.
Phase 6: Billing, Best Practices, & Exam Prep
Billing & Support: Learning how to use “Consolidated Billing” and choosing the right support plan for technical help.
Well-Architected Framework: Following AWS’s 6 pillars to ensure your cloud setup is secure, efficient, and cost-effective.
Shared Responsibility Model: Understanding that AWS secures the “cloud,” but you must secure your “data in the cloud.”
Exam Prep: Reviewing whitepapers and practicing with sample questions to earn your AWS certification.
Conclusion: Mastering the Future
Cloud computing is the engine of modern innovation, turning complex infrastructure into a flexible, on-demand utility. By completing this course, you’ve gained the power to build, secure, and scale global applications with professional efficiency. This roadmap bridges the gap between basic coding and high-level architecture, preparing you for the most in-demand roles in tech. The tools are now in your hands—it’s time to start building the future in the cloud.




