Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Modern applications demand fast, reliable, and repeatable deployments. Manual deployments are error-prone, slow, and difficult to scale. This is where CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) comes in.
In this blog, we’ll walk through building a complete CI/CD pipeline on AWS using CodePipeline, along with CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, IAM, and S3. We’ll also cover architecture, best practices, security, and common interview questions around AWS CI/CD.
By the end, you’ll understand:
- How AWS CodePipeline works
- How CI/CD stages are connected
- How to deploy applications automatically
- Real-world design considerations
What is CI/CD?
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI is the practice of:
- Automatically building code
- Running unit tests
- Validating every code commit
Continuous Deployment (CD)
CD automates:
- Deployment to test or production environments
- Rollbacks in case of failure
- Zero-downtime deployments
Together, CI/CD ensures faster releases, better code quality, and reduced human error.
Why Use AWS for CI/CD?
AWS provides fully managed CI/CD services, meaning:
- No servers to manage
- High availability
- Native integration with AWS services
- IAM-based security
Key AWS CI/CD services:
- AWS CodePipeline – Orchestration
- AWS CodeBuild – Build & test
- AWS CodeDeploy – Deployment
- Amazon S3 – Artifact storage
- IAM – Access control
- CloudWatch – Monitoring & logs
What is AWS CodePipeline?
AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed CI/CD orchestration service that automates the build, test, and deploy phases of your release process.
Key Features
- Event-driven (triggers on code changes)
- Visual pipeline stages
- Supports multiple environments
- Integrates with GitHub, CodeCommit, S3
- Supports manual approvals
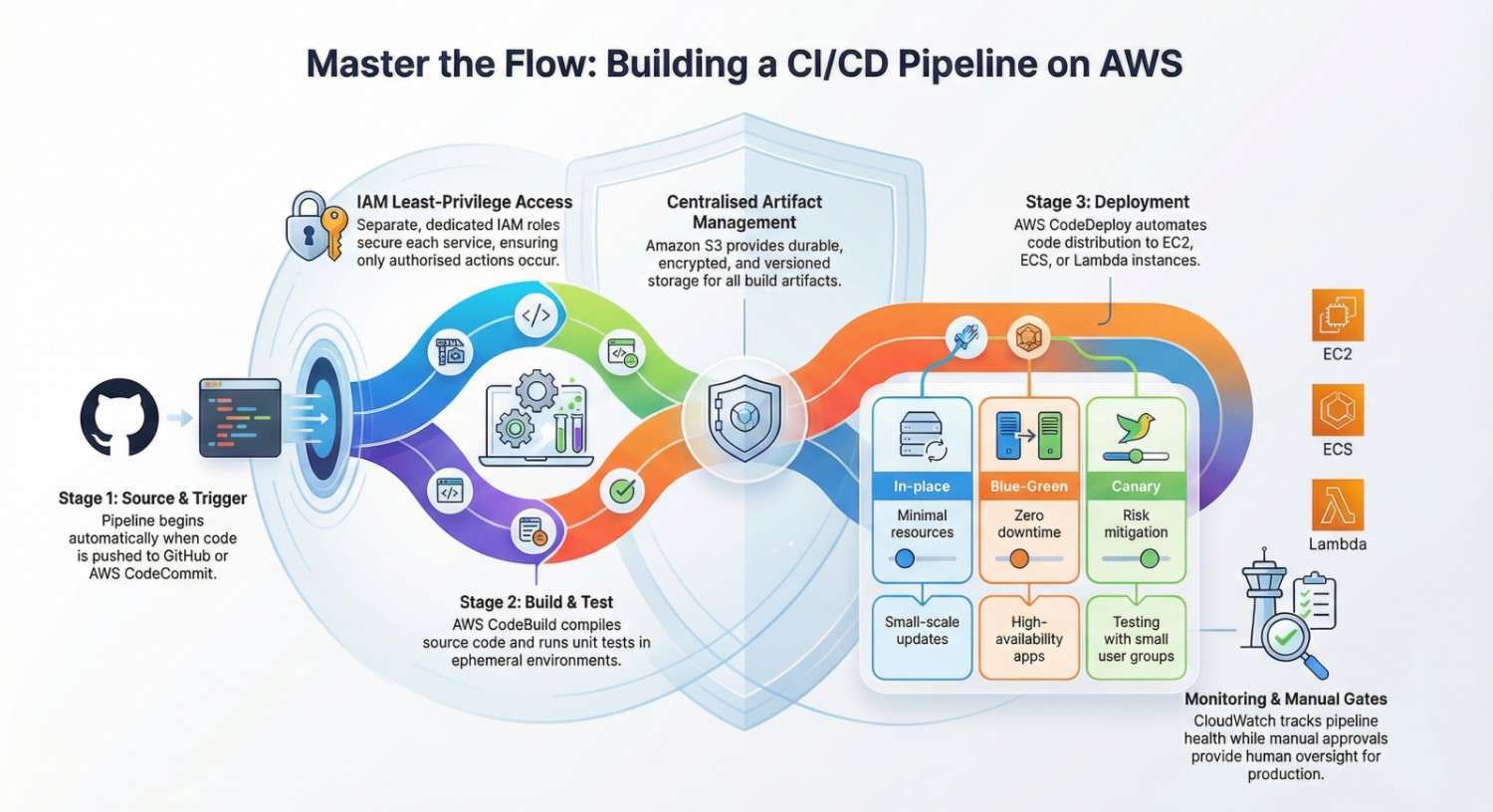
CI/CD Pipeline Architecture on AWS
High-Level Architecture
- Source Stage
- GitHub / CodeCommit repository
- Build Stage
- CodeBuild compiles code and runs tests
- Artifact Storage
- Build artifacts stored in S3
- Deploy Stage
- CodeDeploy deploys to EC2 / ECS / Lambda
Developer → Git Repo → CodePipeline
↓
CodeBuild
↓
S3 Artifacts
↓
CodeDeploy → EC2
Step-by-Step CI/CD Pipeline Setup
Step 1: Source Stage (Git Repository)
The pipeline starts when a developer pushes code to:
Best Practices
- Use branch-based pipelines (dev, staging, prod)
- Protect main/master branches
- Use webhook triggers instead of polling
Step 2: Build Stage Using AWS CodeBuild
AWS CodeBuild compiles source code, runs tests, and produces artifacts.
buildspec.yml Example
version: 0.2
phases:
install:
runtime-versions:
nodejs: 18
build:
commands:
- npm install
- npm test
- npm run build
artifacts:
files:
- '**/*'
Key Concepts
- Build environments are ephemeral
- Pay only for build minutes
- Logs stored in CloudWatch
Step 3: Artifact Management with S3
Build artifacts are stored in Amazon S3.
Why S3?
- Durable
- Versioned
- Encrypted at rest
- Integrated with CodePipeline
Security Tips
- Enable bucket versioning
- Use SSE-S3 or SSE-KMS encryption
- Restrict bucket access via IAM
Step 4: Deployment Using AWS CodeDeploy
AWS CodeDeploy automates deployment to:
- EC2
- ECS
- Lambda
appspec.yml Example (EC2)
version: 0.0
os: linux
files:
- source: /
destination: /var/www/html
hooks:
AfterInstall:
- location: scripts/install.sh
ApplicationStart:
- location: scripts/start.sh
Deployment Strategies
- In-place deployment
- Blue-Green deployment
- Canary deployment
IAM Roles and Permissions
IAM is critical for securing CI/CD pipelines.
Required IAM Roles
- CodePipeline service role
- CodeBuild execution role
- CodeDeploy role
- EC2 instance profile
IAM Best Practices
- Follow least privilege
- Separate roles per service
- Avoid wildcard permissions
- Rotate credentials
Monitoring and Logging
CloudWatch Integration
- CodeBuild logs
- Pipeline execution status
- Deployment health
Alarms
- Build failures
- Deployment failures
- Rollback events
Monitoring ensures quick incident response and pipeline reliability.
Common CI/CD Design Patterns
Multi-Account Pipeline
- Dev account
- Staging account
- Production account
Manual Approval Gates
- Required before production deployment
Infrastructure as Code
- Use CloudFormation or Terraform
- Version infrastructure with application code
Cost Optimization Tips
- Use smaller CodeBuild compute types
- Stop unused pipelines
- Use build caching
- Avoid over-triggering builds
- Clean old S3 artifacts
Security Best Practices
- Encrypt artifacts
- Use IAM roles, not access keys
- Enable CloudTrail
- Scan dependencies during build
- Restrict production deployments
Common AWS Interview Questions (Based on This Pipeline)
Q: What is CodePipeline?
A: A managed CI/CD orchestration service that automates build, test, and deployment workflows.
Q: Difference between CodeBuild and CodeDeploy?
A: CodeBuild compiles and tests code; CodeDeploy handles deployment.
Q: How do you secure a CI/CD pipeline?
A: IAM least privilege, encryption, approvals, logging, and monitoring.
Q: How do you implement rollback?
A: Use CodeDeploy with automatic rollback on failure.
Conclusion
Building a CI/CD pipeline on AWS using CodePipeline enables:
- Faster deployments
- Improved reliability
- Better security
- Scalable DevOps practices
This architecture is production-ready, cost-effective, and highly interview-relevant. Writing and implementing this pipeline demonstrates real-world AWS DevOps experience, not just theoretical knowledge.