If you’re working in modern software development, you’ve likely heard the terms CI/CD pipelines script, how to build CI/CD pipelines, and DevOps CI/CD pipelines more times than you can count.
But in 2026, CI/CD isn’t just a DevOps buzzword it’s the backbone of high-performing engineering teams.
This practical guide will walk you through:
- What CI/CD pipelines really are
- Why they matter more than ever
- How to build CI/CD pipelines step-by-step
- How to write a CI/CD pipelines script
- Best practices for DevOps CI/CD pipelines in 2026
Let’s dive in.
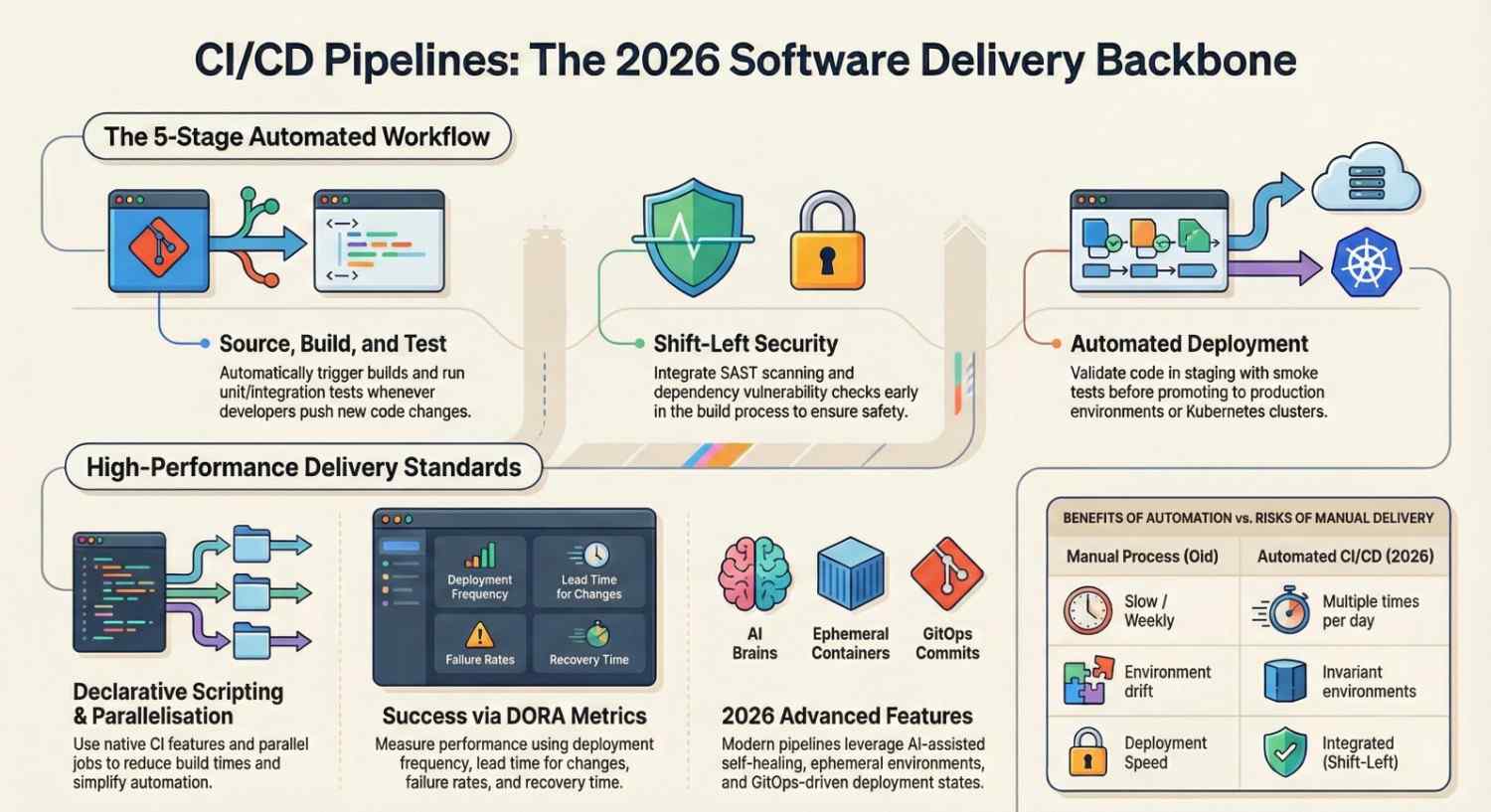
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are CI/CD Pipelines?
CI/CD stands for:
- Continuous Integration (CI) – Automatically building and testing code when changes are pushed
- Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD) – Automatically releasing validated code to staging or production
A CI/CD pipeline is an automated workflow that takes your code from commit → build → test → deploy.
In simple terms:
A CI/CD pipeline removes manual steps between writing code and delivering it to users.
Modern DevOps CI/CD pipelines are built using tools like:
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI/CD
- Jenkins
- CircleCI
Why CI/CD Pipelines Matter in 2026
Software delivery expectations have changed.
Users expect:
- Faster releases
- Fewer bugs
- Zero downtime
- Continuous improvements
Without DevOps CI/CD pipelines, teams struggle with:
- Manual deployments
- Long QA cycles
- Broken builds
- Inconsistent environments
High-performing teams deploy multiple times per day and they rely on automated pipelines to do it safely.
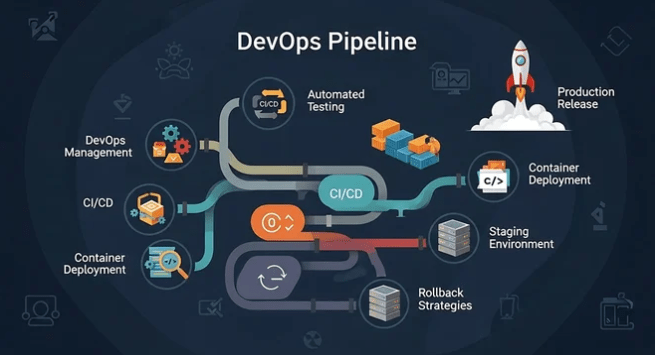
Core Stages of a CI/CD Pipeline
A typical CI/CD pipeline includes:
1️⃣ Source Stage
- Developer pushes code to repository (GitHub, GitLab, etc.)
- Pipeline is triggered automatically
2️⃣ Build Stage
- Dependencies installed
- Application compiled
- Artifacts generated
3️⃣ Test Stage
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- Linting and code quality checks
4️⃣ Security Stage (DevSecOps)
- SAST scanning
- Dependency vulnerability scanning
- Secrets detection
5️⃣ Deploy Stage
- Deploy to staging
- Run smoke tests
- Promote to production
Modern DevOps CI/CD pipelines often include monitoring and rollback automation as well.
How to Build CI/CD Pipelines (Step-by-Step)
Let’s break down how to build CI/CD pipelines from scratch.
Step 1: Choose Your CI/CD Tool
For example:
- Use GitHub Actions if your code is on GitHub
- Use GitLab CI/CD for integrated DevOps workflows
- Use Jenkins for highly customizable enterprise setups
Step 2: Define Your Pipeline Stages
Keep it simple initially:
- Install dependencies
- Run tests
- Build artifact
- Deploy
Avoid overengineering your first pipeline.
Step 3: Write Your CI/CD Pipelines Script
A CI/CD pipelines script defines your automation workflow in YAML or configuration format.
Here’s a simple example using GitHub Actions:
name: CI Pipeline on: push: branches: – main jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: – uses: actions/checkout@v3 – name: Install dependencies run: npm install – name: Run tests run: npm test – name: Build app run: npm run buildThis CI/CD pipelines script:
- Triggers on push
- Installs dependencies
- Runs tests
- Builds the app
That’s the foundation of DevOps CI/CD pipelines.
Step 4: Add Deployment Automation
You can deploy to:
- Cloud VMs
- Containers
- Kubernetes clusters
- Serverless platforms
For containerized deployments, teams often use:
- Docker
- Kubernetes
Step 5: Add Environment Separation
Use:
- Development
- Staging
- Production
Never deploy directly to production without validation.
CI/CD Pipelines Script Best Practices
When writing your CI/CD pipelines script:
✅ Keep It Declarative
Avoid complex shell logic inside scripts. Use native CI features.
✅ Use Caching
Cache dependencies to speed up builds.
✅ Run Jobs in Parallel
Parallelization drastically reduces pipeline time.
✅ Fail Fast
Stop the pipeline as soon as a stage fails.
✅ Store Secrets Securely
Use platform secrets manager never hardcode credentials.
DevOps CI/CD Pipelines Architecture in 2026
Modern DevOps CI/CD pipelines include:
- Infrastructure as Code
- Container-first builds
- Ephemeral environments
- Automated security scanning
- Observability integration
Many teams also integrate:
Advanced CI/CD Concepts
Pipeline as Code
Everything defined in version control.
Benefits:
- Versioned changes
- Peer review
- Rollback capability
GitOps
Deployment state defined in Git.
Tools like Argo CD continuously reconcile cluster state with Git.
Shift-Left Security
Security scans during build not after release.
This is now standard in DevOps CI/CD pipelines.
Common CI/CD Mistakes to Avoid
- Overcomplicating your CI/CD pipelines script
- Running slow integration tests on every commit
- Not separating environments
- Ignoring pipeline metrics
- Manual approval bottlenecks everywhere
Metrics That Matter
High-performing DevOps CI/CD pipelines measure:
- Deployment frequency
- Lead time for changes
- Change failure rate
- Mean time to recovery (MTTR)
These are often called DORA metrics.
Sample Real-World Pipeline Flow
- Developer pushes code
- CI pipeline runs tests
- Docker image built
- Image pushed to registry
- Kubernetes deployment updated
- Argo CD syncs changes
- Monitoring alerts if issues detected
Fully automated. Minimal human intervention.
The Future of CI/CD Pipelines
By 2026, pipelines are becoming:
- AI-assisted
- Self-healing
- Cost-optimized
- Fully observable
- Security-native
The biggest shift?
CI/CD pipelines are evolving into complete software delivery platforms.
Final Thoughts
If you’re learning how to build CI/CD pipelines, start simple:
- Automate builds
- Add automated tests
- Automate deployments
- Improve incrementally
Your CI/CD pipelines script doesn’t need to be perfect on day one.
But every improvement reduces risk, increases speed, and strengthens your DevOps CI/CD pipelines maturity.