Modern software development moves fast. Teams ship features daily, sometimes multiple times per day. But how does code written on a developer’s laptop become a scalable application serving thousands (or millions) of users?
The answer lies in the DevOps toolchain a powerful combination of tools that automate and streamline the journey from code to production.
In this guide, we’ll explain in simple terms how Git, Docker, and Kubernetes work together in modern DevOps.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is the DevOps Toolchain?
The DevOps toolchain is a set of tools used to:
- Manage code
- Automate testing and deployment
- Package applications
- Run them reliably in production
- Scale applications automatically
At the heart of this toolchain are:
- Git – Version Control
- Docker – Containerization
- Kubernetes – Orchestration
Think of it like this:
Git manages your code
Docker packages your app
Kubernetes runs and scales it
Let’s break this down step by step.
Step 1: Git – Managing Code the Smart Way
Before DevOps, teams often shared code manually. That caused confusion, lost work, and conflicts.
What Is Git?
Git is a version control system. It tracks changes in your code and allows multiple developers to work together safely.
Why Git Is Important in DevOps
- Tracks every code change
- Enables collaboration
- Allows branching and merging
- Acts as the “single source of truth”
- Triggers CI/CD pipelines
When a developer pushes code to platforms like GitHub or GitLab, it can automatically start a build and deployment process.
Simple Analogy
Git is like Google Docs for developers. Everyone can work together, track history, and revert mistakes.
Step 2: Docker – Solving “It Works on My Machine”
One of the biggest problems in software development:
“It works on my machine.”
Different environments cause errors:
- Different OS
- Different library versions
- Missing dependencies
What Is Docker?
Docker is a platform that packages your application and its dependencies into a container.
A container includes:
- Your application
- Required libraries
- Runtime
- System tools
This ensures the app runs the same everywhere:
- Developer laptop
- Testing server
- Production cloud
Key Docker Concepts
- Dockerfile – Instructions to build the image
- Docker Image – Blueprint of the app
- Container – Running instance of the image
Why Docker Matters in DevOps
- Environment consistency
- Faster deployments
- Lightweight compared to virtual machines
- Easy scalability
In a DevOps workflow:
- Developer pushes code to Git
- CI system builds a Docker image
- Image is stored in a container registry
Now the application is ready to run anywhere.
Step 3: Kubernetes – Running Containers at Scale
Docker solves packaging. But what happens when:
- You need 10 containers?
- One crashes?
- Traffic suddenly spikes?
- You need zero-downtime updates?
That’s where Kubernetes comes in.
What Is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform. It manages and automates the deployment, scaling, and operation of containers.
It was originally developed by Google and is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.
What Kubernetes Does
- Automatically restarts failed containers
- Scales applications up or down
- Distributes traffic across containers
- Handles rolling updates
- Manages service discovery
Simple Analogy
If Docker is a shipping container, Kubernetes is the port manager that:
- Decides where containers go
- Monitors them
- Replaces broken ones
- Handles traffic
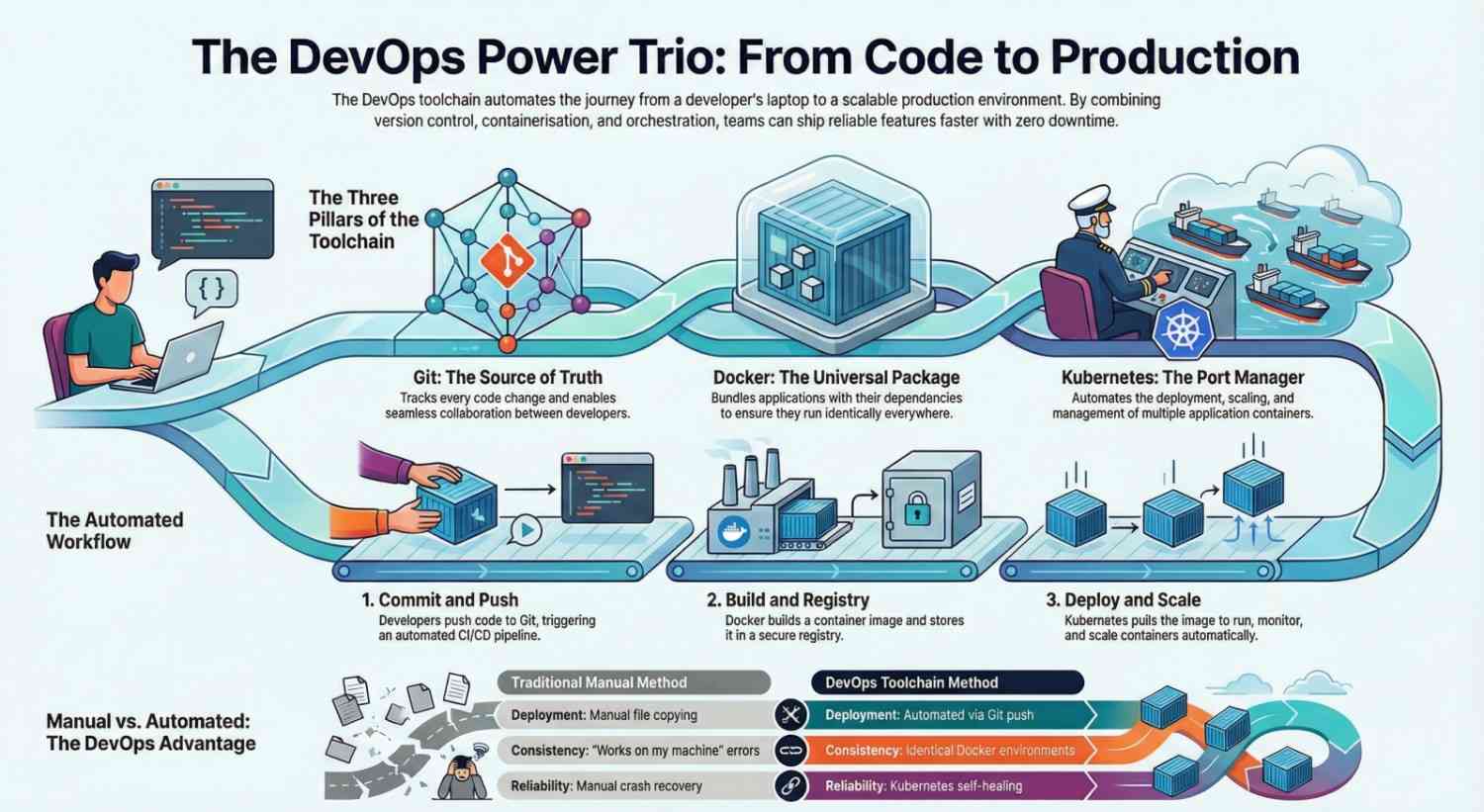
How Git, Docker, and Kubernetes Work Together
Now let’s connect everything.
Here’s a simple DevOps workflow:
1. Developer writes code
Code is stored in a Git repository.
2. Code is pushed
Git triggers a CI/CD pipeline.
3. Docker builds the application
A Docker image is created.
4. Image is stored
The image is pushed to a container registry.
5. Kubernetes deploys it
Kubernetes pulls the image and runs containers.
6. Users access the app
Kubernetes ensures the app stays available and scalable.
Example: Deploying a Web Application
Imagine deploying a Node.js application.
Without DevOps Toolchain:
- Manually copy files to server
- Install dependencies manually
- Restart service manually
- Fix crashes manually
With DevOps Toolchain:
- Push code to Git
- CI builds Docker image
- Kubernetes updates application automatically
- Zero downtime
- Auto-scaling enabled
That’s the power of modern DevOps.
Why This Toolchain Is So Popular
The combination of Git, Docker, and Kubernetes dominates modern software development because it provides:
1. Speed
Automated builds and deployments.
2. Reliability
Self-healing systems and consistent environments.
3. Scalability
Scale applications instantly based on demand.
4. Collaboration
Teams work smoothly across environments.
5. Cloud-Native Support
Works perfectly in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Key DevOps Keywords Covered
This blog ties together essential DevOps concepts:
- DevOps toolchain
- Version control
- Git workflow
- Containerization
- Docker containers
- Kubernetes orchestration
- CI/CD pipeline
- Cloud-native applications
- Container registry
- Infrastructure automation
Final Thoughts
Understanding DevOps becomes much easier when you simplify the roles:
- Git manages code
- Docker packages applications
- Kubernetes runs and scales them
Together, they create a seamless journey:
From writing code → to deploying scalable production systems.
If you’re learning DevOps, mastering these three tools gives you a strong foundation for working with modern cloud-native infrastructure.
- If you want to explore DevOps, start your training here.