Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction.
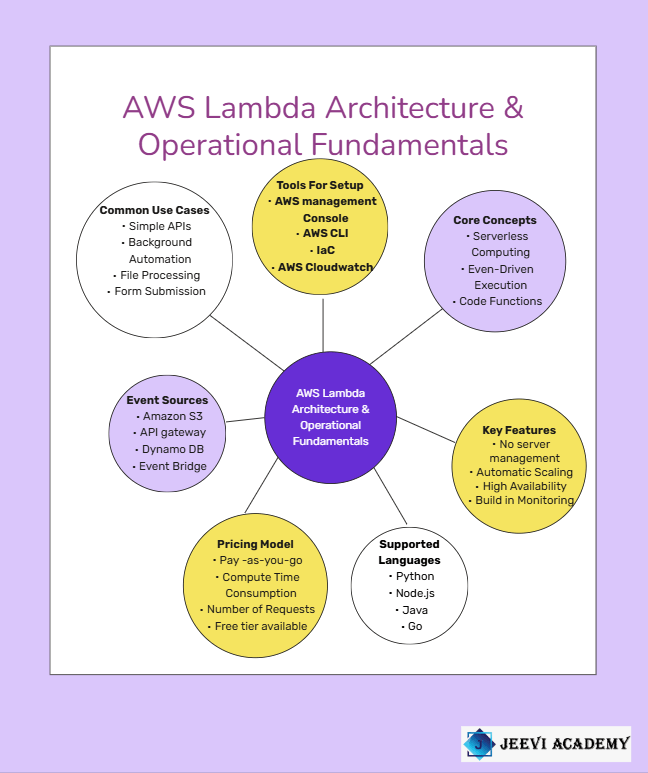
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services that allows developers to run code without having to manage servers, making it an ideal starting point for beginners in cloud computing. With Lambda, developers can focus on writing code while AWS automatically handles the infrastructure, including provisioning, scaling, and managing the underlying servers. This eliminates much of the complexity and overhead associated with traditional server-based applications. AWS Lambda executes code in response to events, which can come from many sources such as Amazon S3, API Gateway, DynamoDB, EventBridge, or even direct function calls.
For beginners, this means that you can build applications that respond automatically to changes in data, user requests, or system events without needing to write complex server management scripts. One of the key advantages of AWS Lambda is that it follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, meaning that you only pay for the compute time your code consumes and the number of requests made, which can be extremely cost-effective for small projects, prototypes, or learning exercises. AWS Lambda supports multiple programming languages, including Python, Node.js, Java, Go, and more, allowing beginners to use a language they are already familiar with while learning serverless concepts.
The service also includes a free tier, providing one million requests and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month, which is sufficient for experimenting, testing, and running low-traffic applications without incurring any cost. Beginners can create functions through the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or by using Infrastructure as Code tools, and they can trigger these functions through various events or scheduled tasks. Lambda automatically scales based on the number of events, handling everything from a single request to thousands per second, which means that beginners do not need to worry about manual scaling or performance tuning. Monitoring and logging are built in through AWS CloudWatch, allowing beginners to track function performance, troubleshoot errors, and understand execution patterns easily.
AWS Lambda also integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, making it possible to build complex, event-driven architectures without managing servers. For beginners, this means a smoother learning curve and faster development cycles, as they can focus on solving business problems rather than infrastructure challenges. Learning AWS Lambda introduces beginners to core cloud concepts such as event-driven programming, serverless architectures, automatic scaling, and cost optimization.
By understanding how Lambda works, beginners can also explore advanced features such as provisioned concurrency, environment variables, ephemeral storage, and VPC integration, gradually increasing their knowledge without overwhelming complexity. Overall, AWS Lambda is a powerful yet approachable service for beginners, combining ease of use, flexible pricing, and strong integration with the broader AWS ecosystem, making it an excellent starting point for anyone looking to enter cloud computing, develop serverless applications, or experiment with automated and event-driven solutions.
What Is AWS Lambda?
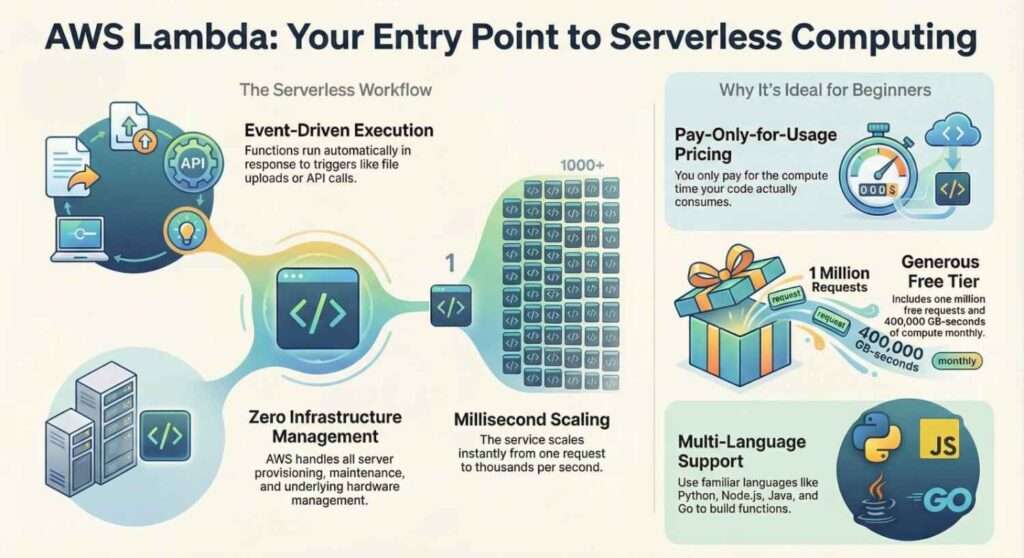
AWS Lambda lets you run small pieces of code, called functions, in response to events. These events can come from services like Amazon S3, API Gateway, DynamoDB, or EventBridge. For example, a Lambda function can automatically resize an image when it is uploaded to S3 or process a request when someone calls an API.
How AWS Lambda Works
When an event occurs, AWS Lambda automatically runs your function. It allocates the required compute resources, executes the code, and then shuts everything down once the task is complete. This happens within milliseconds and scales automatically, whether your function runs once a day or thousands of times per second.
Why Beginners Should Use AWS Lambda
One of the biggest advantages of AWS Lambda is simplicity. Beginners don’t need deep knowledge of servers or infrastructure. Lambda is also cost-effective because you only pay for the time your code runs. There is even a free tier that allows new users to experiment without spending money.
Supported Languages
AWS Lambda supports several popular programming languages, including Python, JavaScript (Node.js), Java, Go, and others. This makes it easy for beginners to start using Lambda with a language they already know.
Common Use Cases
Beginners often use AWS Lambda for tasks like building simple APIs, automating background jobs, processing files, handling form submissions, and creating event-driven applications. These use cases help new developers understand serverless concepts quickly.
Getting Started with AWS Lambda
To start with AWS Lambda, you need an AWS account. From the AWS Management Console, you can create a Lambda function, choose a runtime, write or upload your code, and configure a trigger. AWS also provides built-in monitoring through CloudWatch to help you track performance and errors.
Final Thoughts
AWS Lambda is an excellent entry point into cloud computing and serverless architecture. It removes much of the complexity associated with traditional servers and allows beginners to focus on writing code and building applications. With its ease of use, automatic scaling, and cost-efficient pricing model, AWS Lambda is a powerful tool for anyone starting their cloud journey.
- For more information about AWS Lambda, you can refer to Jeevi’s page.





