Introduction.
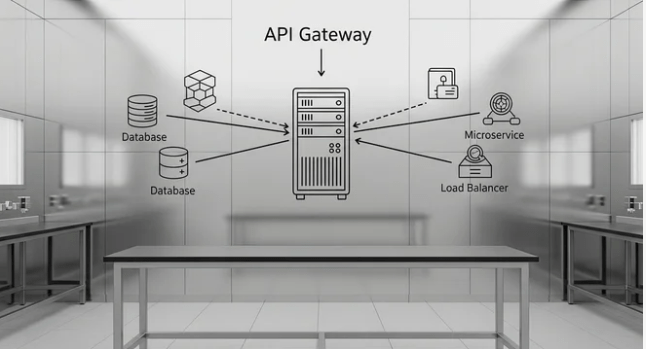
Building an API Gateway with Lambda integration is one of the most powerful and flexible ways to create serverless applications on AWS. Amazon API Gateway serves as a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale. By integrating it with AWS Lambda, developers can run backend code without provisioning or managing any servers.
This combination enables a completely serverless architecture, reducing operational complexity and cost while providing high scalability and availability. In this setup, API Gateway acts as the entry point for client requests, while AWS Lambda functions handle the business logic, process data, and return responses. The API Gateway receives HTTP or RESTful requests from clients, transforms and validates them if needed, and then triggers the corresponding Lambda function. Lambda, in turn, executes the code written in languages such as Python, Node.js, Java, or Go, and sends the response back through the API Gateway to the user.
This integration pattern decouples the frontend and backend, allowing developers to focus on writing code that matters instead of managing servers. It also allows easy implementation of microservices, where each API endpoint can invoke a separate Lambda function performing a specific task. Security can be enforced using AWS IAM roles, Cognito user pools, or API keys, ensuring controlled access to backend resources. Additionally, developers can set throttling limits and caching policies to improve performance and protect against abuse.
The pay-per-use pricing model of both API Gateway and Lambda ensures cost efficiency since you only pay for the requests served and the compute time used. This makes it an excellent choice for startups, enterprises, and developers building APIs for mobile apps, web services, or IoT devices. The integration also supports versioning and staging, allowing safe deployment of new API versions without disrupting production users. With API Gateway’s support for both REST APIs and HTTP APIs, developers can choose between feature richness and cost optimization based on their needs.
Lambda integration simplifies continuous deployment pipelines, as new code can be deployed automatically without server reconfiguration. Logging and monitoring are also seamless through CloudWatch, enabling easy tracking of metrics, request counts, and error rates. The system’s event-driven nature ensures that resources are used efficiently, scaling automatically with incoming traffic. This architecture aligns perfectly with modern DevOps and agile development practices. Building an API Gateway with Lambda integration also encourages modularity and reusability in code design. Each Lambda function can be independently updated, tested, and deployed, allowing rapid iteration and innovation.
Furthermore, it simplifies backend communication with other AWS services such as DynamoDB, S3, or SNS, using IAM roles for secure and direct access. The combination also supports various payload formats, including JSON, binary data, and custom mappings, offering flexibility for different use cases. Developers can test and simulate API calls within the AWS Management Console, speeding up development cycles. Documentation generation through API Gateway further enhances developer collaboration and consumer understanding. Whether it’s building a simple CRUD API or a complex data processing pipeline, the integration provides a robust and scalable foundation. Error handling and response transformation are easily managed within API Gateway, reducing code complexity inside Lambda.
Additionally, CORS configuration allows seamless communication with web frontends hosted on different domains. By leveraging this integration, developers can build secure, reliable, and high-performing APIs in a fraction of the time traditional server-based architectures would require. It is a cornerstone of serverless application design, empowering developers to innovate faster, deploy continuously, and scale effortlessly. Overall, building an API Gateway with Lambda integration represents the modern paradigm of API development, enabling organizations to deliver responsive, scalable, and cost-effective digital solutions efficiently.

Lab Steps
Step 1: Sign to the AWS Management Console
1. Click on the Open Console button, and you will get redirected to AWS Console in a new browser tab.
2. Copy your User Name and Password in the Lab Console to the IAM Username and Password in the AWS Console and click on the Sign in button.
Step 2:Create a Lambda Function
1.Navigate to the services menu at the top, then click on lambda under the compute section.
2.Click on the Create Function button.
- Choose: Author from Scratch.
- Function Name: JeeviAPI.
- Runtime should be Python 3.12.
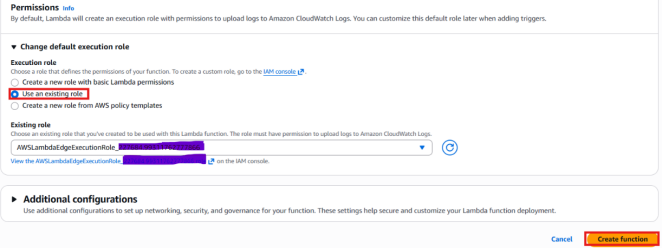
- Executing Role: In the permissions section, choose Use an existing role.
- Existing Role: AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole<random.number>.
Then click on Create function.
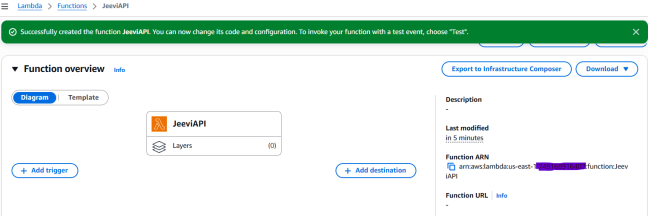
3.Once the Lambda function is created successfully , it will like the screenshot below.
Step 3: Create an API
1. Navigate to the services menu at the top, select API Gateway under the Networking & Content Delivery section.
2. Click on Get Started (if this is your first time).
If a pop-up appears asking to create your first API, choose REST API and continue.

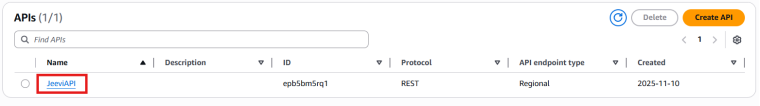
3. Choose Create API → then select New API under REST API
4. In the settings, enter the API name as JeeviAPI (or any name you prefer).
Leave the other settings as default.
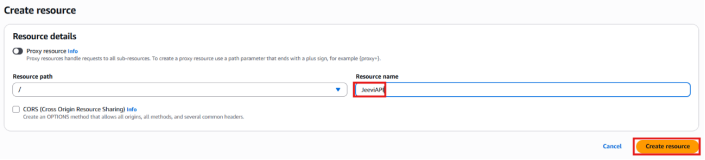
Step 4: Creating a Resource
- Once your API is created, select it from the list (for example, JeeviAPI).
- From the left-side panel or the Actions menu, choose Create Resource.
Step 5: Creating a Method
1.After creating your resource, click on Create Method.
2. From the dropdown list, select GET (or whichever method type you need).
3. Choose the Integration type as Lambda Function.
4. Make sure the Region is set to us-east-1 (N. Virginia).
5. In the Lambda Function field, type the function name — for example, JeeviAPIs.
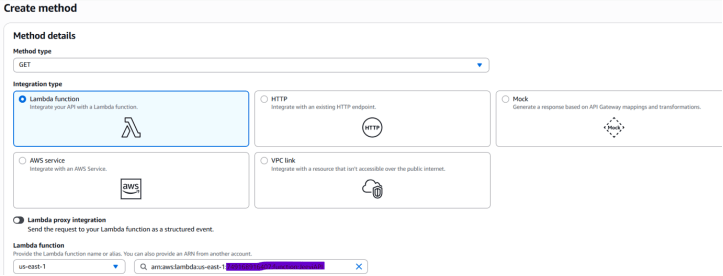
6.Click Create Method.
Stage 6: Deploy the API
- After you’ve created the resource and method successfully, you can now deploy the API.
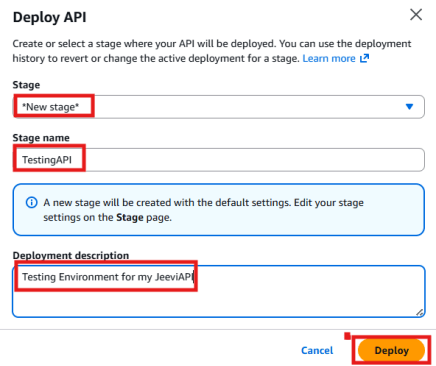
- Then select Deploy API.
- Under Deployment stage, choose New Stage.
- In the Stage name, enter testingAPI (or any name you prefer).
- In the Stage description, you can write something like Testing environment for my JeeviAPI.
- Click Deploy.
Once the API has been deployed, go to the Stages section — you’ll see your API stage listed (for example, testingAPI).
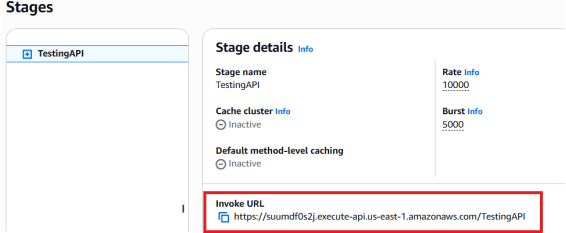
- Copy the Invoke URL displayed under your stage.
- Now a 10. Open a new browser tab or use an API testing tool like Postman.
- Paste the full URL and send a GET request.dd your resource name (for example, /JeeviAPI) to the end of the URL.
- You should see a response like this:
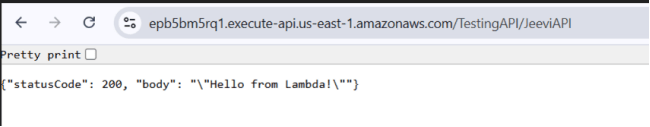
You have successfully created a Lambda function, connected it with API Gateway, deployed it, and tested the Invoke URL to get a live response from your AWS Lambda function.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, building an API Gateway with Lambda integration represents a modern, efficient, and scalable approach to developing and deploying APIs in a fully serverless environment. This architecture eliminates the need for traditional servers, allowing developers to focus purely on writing business logic while AWS handles infrastructure management, scaling, and fault tolerance.
The seamless interaction between API Gateway and Lambda simplifies backend operations, enhances security, and provides fine-grained control over request handling, authentication, and performance optimization. With features like automatic scaling, pay-per-use pricing, and native integrations with other AWS services, this solution ensures both cost-effectiveness and high availability. It empowers developers to create modular, event-driven, and microservice-based architectures that adapt easily to changing requirements. Ultimately, the combination of API Gateway and Lambda offers a powerful foundation for building robust, secure, and responsive APIs that support the needs of modern web, mobile, and IoT applications delivering speed, flexibility, and innovation without the burden of managing infrastructure.
- For more information about AWS API Gateway, you can refer to Jeevi’s page.