In today’s world of cloud computing, serverless technology has become increasingly popular. AWS Lambda is one of the leading serverless services available to developers and IT professionals. It allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. This makes development faster, more scalable, and cost-efficient.
Creating a Lambda function is the first step toward leveraging this serverless architecture. A Lambda function is essentially a piece of code that executes in response to specific triggers. These triggers can include events from other AWS services, HTTP requests, or scheduled timers. The beauty of Lambda is that it automatically handles the infrastructure for you. Developers no longer need to worry about server maintenance, scaling, or high availability.
Once created, Lambda functions can be tested using different methods to ensure they work as expected. Testing is a crucial step because it verifies the correctness of the function’s logic and integration. AWS provides a console to manually invoke functions and check the output. You can also use automated testing with event simulations for more complex scenarios.
Testing helps identify errors, validate responses, and improve overall code quality. Lambda functions can be written in multiple programming languages such as Python, Node.js, Java, or Go. The choice of language depends on the application requirements and developer preference. Event-driven architecture allows Lambda functions to respond in real-time to data changes or API calls. This capability makes Lambda ideal for microservices, backend processing, and automation tasks.
Monitoring and logging are integrated through AWS CloudWatch, providing insights during testing. Lambda also scales automatically, running multiple instances of your function in parallel if needed. This serverless approach reduces operational overhead while increasing reliability. Testing Lambda functions ensures that scaling and performance behave as expected under real-world conditions.
It is also important to validate permissions, environment variables, and external service connections. Developers can iterate quickly, make changes, and re-test without downtime. By creating and testing Lambda functions, teams can build robust serverless applications efficiently. It also encourages best practices such as modular design and event-driven development. Understanding Lambda testing prepares developers for real-world production deployments.
Creating a Lambda function and testing it is a critical skill for modern cloud developers.
It combines automation, scalability, and efficiency, enabling developers to focus on writing code rather than managing servers.
Mastering this process lays the foundation for building advanced serverless applications on AWS.

Lab Steps
Step 1: Sign to the AWS Management Console
1. Click on the Open Console button, and you will get redirected to AWS Console in a new browser tab.
2. Copy your User Name and Password in the Lab Console to the IAM Username and Password in the AWS Console and click on the Sign in button.
Step 2:Create a lambda function
1. Make sure your AWS region is selected as US East (N. Virginia).
2. Navigate to the services menu and click on the Lambda under the computes section.
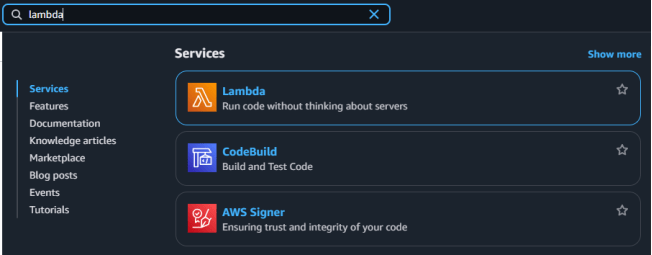
3. Click on the create a function button.

- Choose Authorized from scratch.
- Function Name : Enter myfirstlambda.
- Runtime : Select Python 3.14.
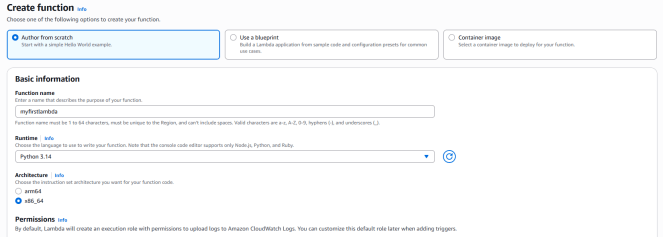
- Click on the change default execution role. Under this , Select Use an executive role and select lambda_Role_<Random_Number>.
- This role has been already created for you.
- Click on create function button.
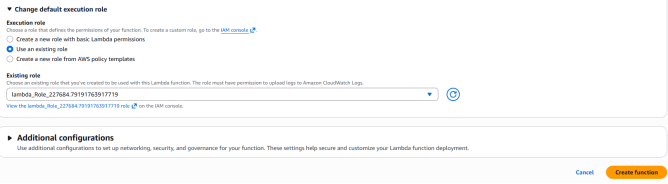
4. Your Lambda function will be created.
STEP 3 : Invoking the function with Test Event.

- Move downwards on the interface until the built-in code editor is visible.
- Access the editor by double-clicking the lambda_function.py file located on the left panel.
- Alter the function’s main content to be “Hello Lambda!” rather than “Hello from Lambda!”. Subsequently, press the “Deploy” button.
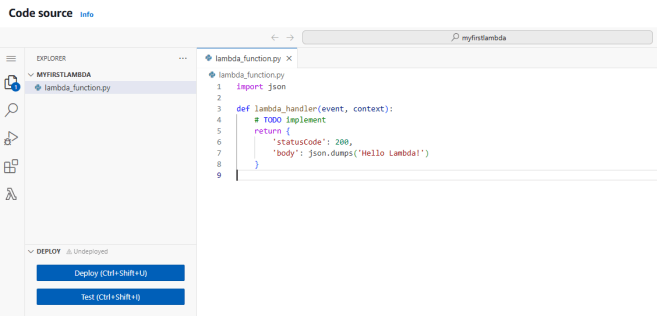
- Initiate a code verification by clicking “Test”. It is necessary to set up a test event configuration initially.
- Provide “myfirstevent” as the identifier for the event and then select the “Save” option.
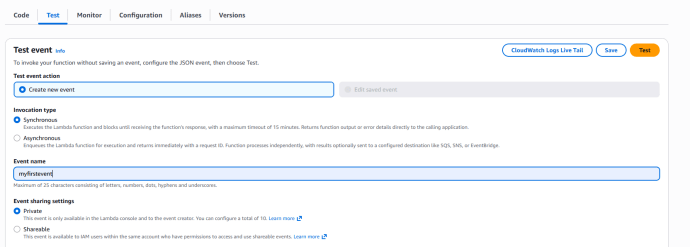
- Click on the Test button again to test the code.
- You will get a Execution result as successful if everything worked correctly.
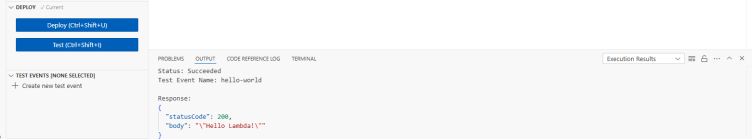
- Here, the status code -200, means that the request was received and is being processed.

Conclusion
- Lambda makes running code serverless and hassle-free.
- Functions can be created and tested in just a few steps.
- Test events help verify results instantly.
- Great for beginners to build event-driven applications.
For more information about AWS Lambda, you can refer to Jeevi’s page.





