Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction.
Managing servers manually can be time-consuming, repetitive, and prone to human error. Imagine having multiple servers and needing to install software, update packages, or configure services on each of them one by one. It’s not only tedious but also increases the risk of mistakes. This is where automation tools like Ansible come in, saving time and making server management effortless.
Ansible is an open-source automation tool that allows system administrators, developers, and DevOps engineers to manage multiple servers from a single control node. It uses simple, human-readable YAML files called playbooks to automate tasks across servers, removing the need to log into each machine individually. Unlike other tools, Ansible does not require agents to be installed on managed nodes, which makes it lightweight and easy to deploy.
If you are new to Ansible, starting from scratch might seem daunting. You may wonder where to install it, how to configure connections, or how to execute commands on remote servers safely. This guide is designed specifically for beginners who want to move from zero knowledge to practical Ansible usage quickly. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a fully functional Ansible setup and be able to manage at least two servers with ease.
We will begin by installing Ansible on your control node, which is the main machine from which you will execute commands. Next, we will prepare the managed nodes, the servers that Ansible will control. Ensuring proper SSH connectivity and Python availability is essential for smooth communication between your control node and managed servers.
Once the setup is complete, we’ll dive into configuring the Ansible inventory file. This file keeps track of all servers you want to manage and allows Ansible to know where to send commands. You’ll learn how to define hosts, groups, and user credentials in a simple, organized way.
After the inventory is set up, we will test the connection between the control node and the managed nodes using Ansible’s built-in modules. The “ping” module, for example, is a quick way to confirm that your servers are reachable and ready for automation.
Finally, this tutorial will demonstrate running basic Ansible commands across multiple servers at once. You’ll understand how to execute tasks, gather system information, and even perform updates without logging into each server individually. These foundational skills will prepare you to explore more advanced Ansible playbooks and automation workflows in the future.
By the end of this guide, you’ll see how much easier server management becomes with automation. Tasks that previously took hours can now be executed in minutes. You’ll gain confidence in managing infrastructure, reducing errors, and scaling operations efficiently. Ansible empowers you to focus on higher-level tasks instead of repetitive manual work.
Whether you are a developer, system administrator, or someone exploring DevOps, learning Ansible is an essential step toward modern infrastructure management. This guide ensures that even complete beginners can follow along and achieve practical results quickly.
With step-by-step instructions, clear examples, and helpful tips, this tutorial will take you from a novice to someone capable of managing multiple servers efficiently. You don’t need prior experience in server management or automation. All that’s required is curiosity, a control machine, and a couple of servers to practice on.
Throughout this guide, we will provide commands, configuration examples, and troubleshooting tips to ensure that you can replicate the setup easily. You’ll also learn best practices to avoid common mistakes while working with Ansible, ensuring a smooth learning experience.
By combining theory with hands-on practice, you will gain not only the ability to connect servers but also the confidence to automate repetitive tasks in your own environment. Ansible’s simplicity and power will help you embrace automation with minimal effort.
So, if you’re ready to move from manual server management to automated efficiency, this guide is your perfect starting point. Let’s take the first step and learn how to install Ansible, configure your servers, and start managing them like a pro.
By the time you finish reading, you’ll have a complete setup ready for real-world automation, opening doors to more advanced Ansible techniques and complex playbooks.
Your journey from zero to Ansible starts here, and this guide will make sure it’s easy, practical, and effective.
PART 1: Install Ansible (Control Node)
Step 1: Update your system
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y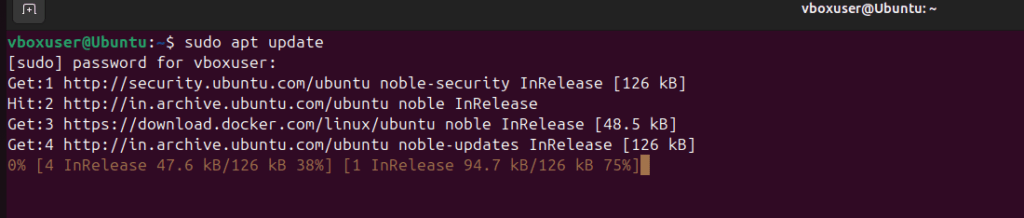
Step 2: Install Ansible
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt install ansible -y
For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo dnf install epel-release -y sudo dnf install ansible -yStep 3: Verify installation
ansible –version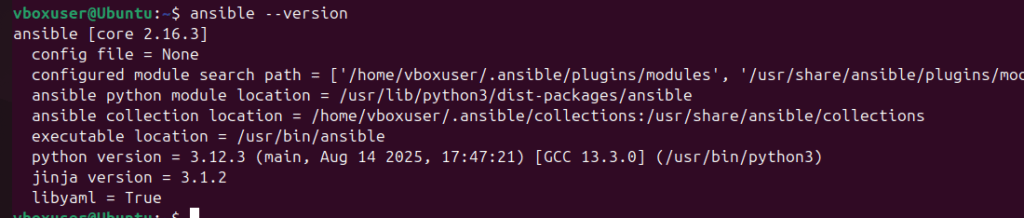
PART 2: Prepare Managed Node (Target Machine)
You need SSH access and Python installed.
Step 1: Install Python
(Already installed on most Linux machines)
sudo apt install python3 -y # Ubuntu/Debian sudo dnf install python3 -y # RHEL/CentOS
Step 2: Make sure SSH is running
sudo systemctl status ssh
If not installed:
sudo apt install openssh-server -y # Ubuntu/DebianPART 3: Set Up SSH Key (Passwordless Login)
Step 1: Generate SSH key on Control Node
ssh-keygen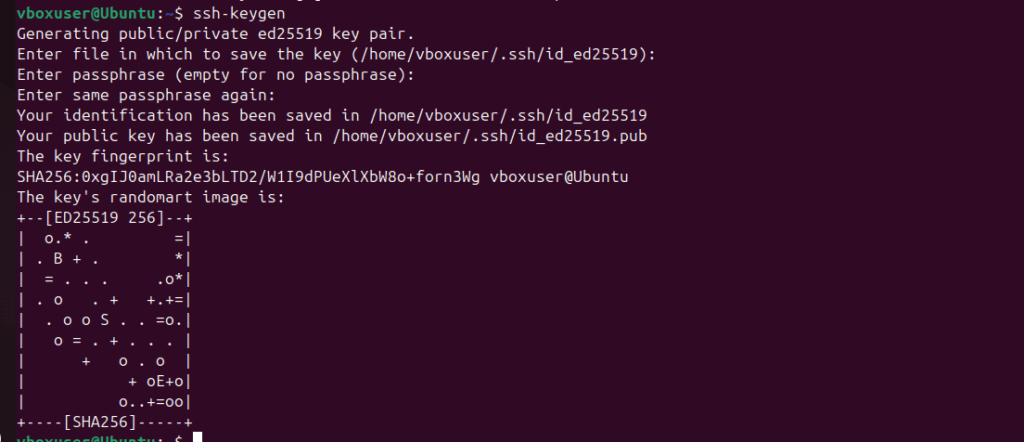
Press Enter for all prompts.
Step 2: Copy the key to the Managed Node
ssh-copy-id user@managed_node_ipExample:
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
Step 3: Test SSH
ssh user@managed_node_ipIf you can log in without password, it works.
PART 4: Configure Ansible Inventory.
Step 1: Edit /etc/ansible/hosts
sudo nano /etc/ansible/hosts
Add your managed node:
[myservers] server1 ansible_host=192.168.1.20 ansible_user=ubuntu
Save and exit.
PART 5: Test Ansible Connection
Ping the target machine:
ansible myservers -m pingIf successful, you get:
{ “ping”: “pong” }Summary
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Install Ansible on control node |
| 2 | Ensure Python + SSH on managed node |
| 3 | Configure passwordless SSH |
| 4 | Add node in Ansible inventory |
| 5 | Test connection with ansible -m ping |
Conclusion.
In conclusion, setting up Ansible and connecting two servers doesn’t have to be complicated. By following the steps outlined in this guide from installing Ansible on your control node, preparing the managed nodes, configuring SSH access, and setting up the inventory file you now have a solid foundation for automating server management.
Ansible simplifies repetitive tasks, reduces human error, and gives you the power to manage multiple servers from a single control point. The ability to run commands, update software, and configure systems across machines simultaneously not only saves time but also makes your workflow more efficient and reliable.
As a beginner, you’ve taken the first crucial step toward mastering infrastructure automation. From here, you can explore writing playbooks, managing larger server groups, and automating complex workflows. The skills you’ve learned will grow with you, whether you’re a system administrator, developer, or aspiring DevOps engineer.
Remember, automation is about making your life easier and your infrastructure more predictable. With Ansible, even the most repetitive and error-prone tasks become simple and consistent. Keep experimenting, practicing, and expanding your playbooks over time, managing servers will feel effortless.
Ultimately, the journey from zero to Ansible is just the beginning. By embracing automation, you’re not just saving time; you’re also building a skill set that is in high demand in today’s IT and DevOps landscape. Now that your servers are connected and ready, the possibilities for automation are endless.
- For more information about Ansible, you can refer to Jeevi’s page.