Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
As organizations accelerate cloud adoption, securing the AWS DevOps pipeline has become critical. While DevOps improves speed and agility, it can also introduce security risks if not properly managed. Misconfigured IAM roles, exposed secrets, insecure containers, and vulnerable dependencies are common attack vectors.
This guide explains how to secure your CI/CD pipeline on AWS using proven tools and strategies following a DevSecOps approach.
Why Securing Your AWS DevOps Pipeline Matters
A compromised CI/CD pipeline can lead to:
- Deployment of malicious code
- Credential leakage
- Infrastructure takeover
- Data breaches
Modern cloud-native environments require security at every stage not just at production.
That’s where DevSecOps on AWS comes in: integrating security into the entire development lifecycle.
Identity & Access Management (IAM) – The Foundation
The first step in AWS DevOps pipeline security is proper access control.
Use:
- AWS Identity and Access Management for least-privilege access
- Role-based access for CI/CD services
- Temporary credentials using STS
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Best Practices:
- Avoid using root accounts
- Use IAM roles instead of long-term access keys
- Rotate credentials automatically
- Use IAM Access Analyzer to detect risky policies
Secure Your CI/CD Pipeline
If you are using AWS-native DevOps tools:
Security Strategies:
- Enable encryption at rest (S3 artifact buckets)
- Use private VPC builds in CodeBuild
- Restrict who can modify pipelines
- Enable CloudTrail logging for audit trails
Enable:
- Artifact integrity checks
- Approval stages before production deployment
- Manual review gates for sensitive environments
Secrets Management
Hardcoding secrets in code is one of the biggest DevOps security mistakes.
Use:
- AWS Secrets Manager
- AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store
Best Practices:
- Rotate secrets automatically
- Store database passwords, API keys, tokens securely
- Grant secrets access via IAM roles only
- Never store secrets in Git repositories
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security
Many teams use:
Secure Your IaC:
- Scan templates before deployment
- Use policy-as-code tools (OPA, Checkov)
- Validate S3 bucket policies
- Block public access configurations
Integrate IaC security scanning into your CI pipeline.
Container & Kubernetes Security
If using containers with:
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry
Secure Containers by:
- Scanning images for vulnerabilities
- Using minimal base images
- Enforcing image signing
- Enabling runtime security policies
Enable ECR image scanning and use Kubernetes RBAC properly.
Automated Security Testing in CI/CD
Integrate these security checks into your pipeline:
- SAST (Static Application Security Testing)
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing)
- Dependency scanning
- Container scanning
AWS security services to integrate:
- Amazon Inspector
- AWS Security Hub
- Amazon GuardDuty
Shift security left test early and automatically.
Monitoring, Logging & Incident Response
Visibility is key to securing your AWS DevOps pipeline.
Use:
Implement:
- Real-time alerts
- Log retention policies
- Centralized logging
- Automated response via Lambda
Create automated incident playbooks for faster mitigation.
Zero Trust & Network Security
- Use VPC endpoints
- Restrict public internet access
- Implement Security Groups & NACL rules
- Use private subnets for build servers
Consider implementing a Zero Trust architecture model.
DevSecOps Culture & Governance
Tools alone are not enough.
Build a culture of:
- Security awareness training
- Secure code reviews
- Regular audits
- Compliance validation
Encourage shared responsibility between DevOps and Security teams.
Common AWS DevOps Pipeline Security Mistakes
- Over-permissive IAM policies
- Storing secrets in GitHub
- No vulnerability scanning
- Skipping approval gates
- No monitoring or alerting
Avoid these to strengthen your pipeline.
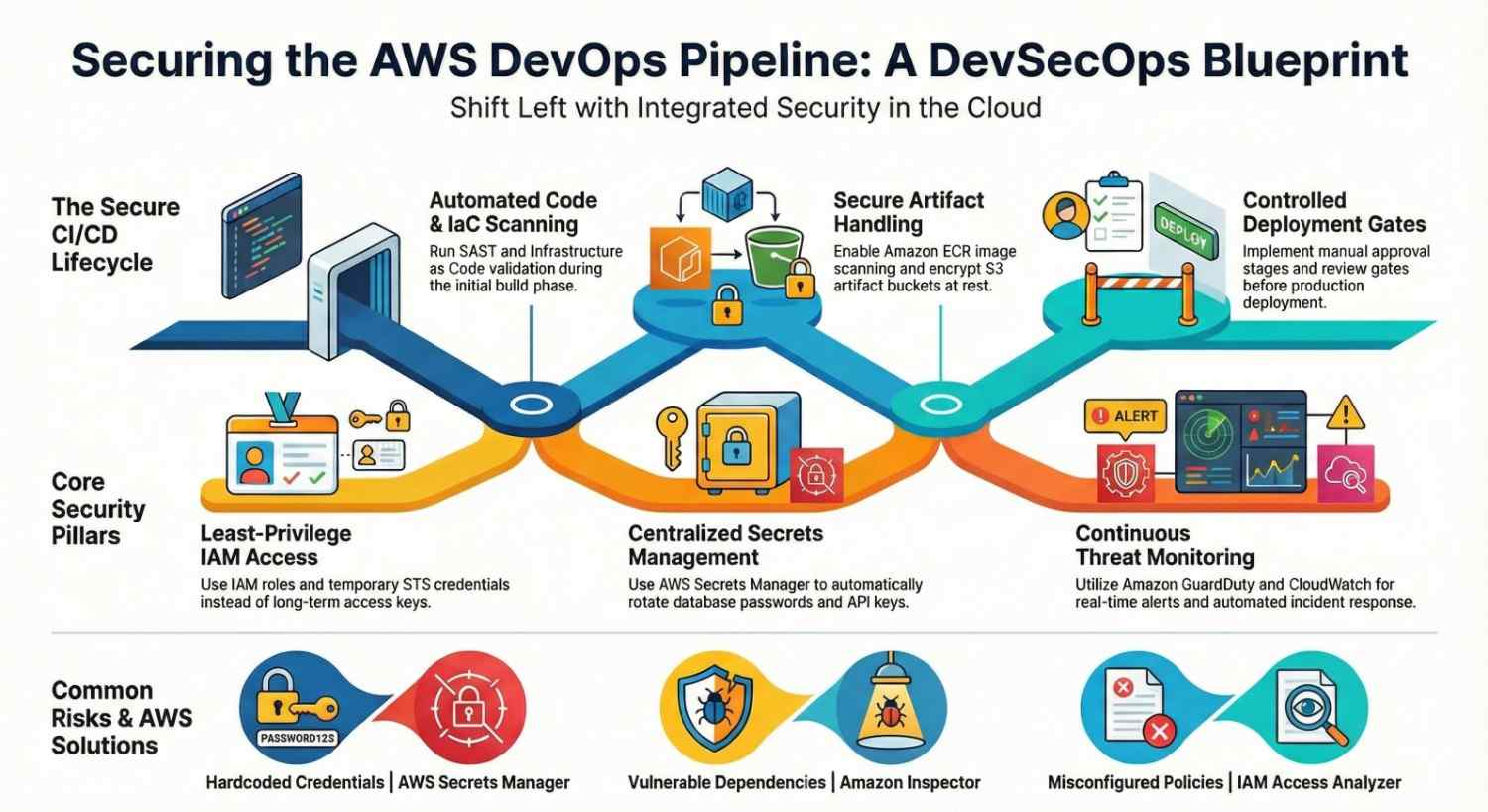
Final Architecture Example (Secure AWS CI/CD Flow)
- Developer pushes code
- CodePipeline triggers
- CodeBuild runs SAST + dependency scan
- IaC templates validated
- Secrets pulled securely
- Container scanned in ECR
- Approval stage
- Deployment to EKS
- Monitoring via CloudWatch & GuardDuty
Conclusion
Securing your AWS DevOps pipeline requires a layered approach:
- Identity security
- Secrets management
- IaC validation
- Automated security testing
- Continuous monitoring
By integrating AWS security tools into your CI/CD workflows, you transform DevOps into DevSecOps on AWS delivering faster, safer, and more reliable software.
- If you want to explore DevOps, start your training here.
- If you want to explore AWS, start your training here.