Introduction:
Modern AI models like Transformers, BERT, and GPT are extremely good at
understanding language. One of the main reasons behind this success is a powerful mechanism called Multi-Head Attention.
Multi-Head Attention allows a model to look at the same sentence in different ways at the same time, helping it understand meaning, context, and relationships between words more accurately.
In this blog, we will explain what multi-head attention is, how it works, and why it is so important — all in simple English.

What is Attention?
Before understanding multi-head attention, let’s briefly understand attention.
Attention helps the model decide:
“Which words should I focus on to understand the current word?”
Example:
Sentence:
“The cat sat on the mat because it was tired.”
To understand “it”, the model must focus on:
● cat, not mat
Attention helps make this decision.
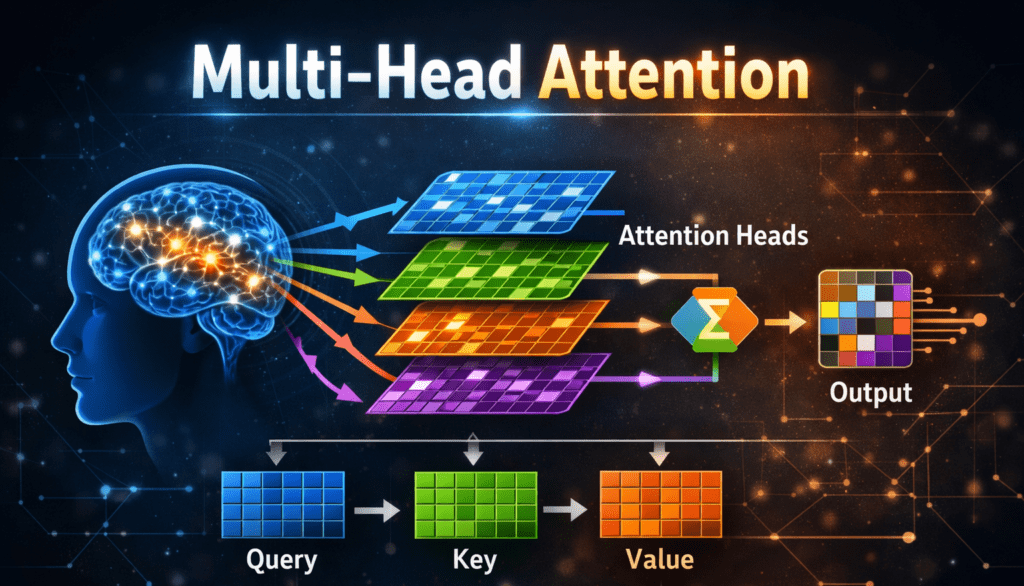
What is Multi-Head Attention?
Multi-Head Attention means:
Instead of using one single attention mechanism, the model uses
multiple attention heads in parallel.
Each head:
● Focuses on different parts of the sentence
● Learns different types of relationships
All heads work together to give a richer understanding of the text.
Simple Definition:
Multi-Head Attention is a technique where multiple attention mechanisms run
in parallel to capture different relationships and meanings in a sentence.
Why Do We Need Multiple Heads?
Using only one attention head is like:
● Looking at a picture with one eye
Using multiple heads is like:
● Looking with both eyes and a microscope
Each head can focus on:
● Grammar (subject–verb)
● Meaning (context)
● Long-distance relationships
● Word importance
Easy Example:
Sentence:
“The student who studied hard passed the exam.”
Different attention heads might focus on:
● Head 1 → student ↔ passed
● Head 2 → studied ↔ hard
● Head 3 → exam ↔ passed
All these views are combined to understand the sentence better.
How Multi-Head Attention Works (Step-by-Step):
Step 1: Create Query, Key, and Value
Each word is converted into three vectors:
● Query (Q) – what the word is looking for
● Key (K) – what the word offers
● Value (V) – the actual information
Step 2: Split into Multiple Heads
Instead of one big Q, K, V:
● They are split into multiple smaller sets
● Each set forms one attention head
Example: 8 heads → 8 different attention views
Step 3: Attention in Each Head
Each head:
● Calculates attention scores
● Focuses on different word relationships
● Produces its own output
Step 4: Combine the Heads
● Outputs from all heads are concatenated
● Passed through a final linear layer
● Result = final attention output
Self-Attention vs Multi-Head Attention:
Self-Attention:
- One attention mechanism
- Single view
- Limited understanding
Multi-Head Attention:
- Multiple attention mechanisms
- Multiple views
- Rich understanding
Multi-Head Attention in Transformers:
In Transformer models:
● Encoder uses multi-head self-attention
● Decoder uses:
○ Masked multi-head self-attention
○ Encoder-decoder attention
This structure allows Transformers to:
● Understand context
● Generate fluent text
● Handle long sentences
Multi-Head Attention is an improved version of self-attention.
Advantages of Multi-Head Attention:
- Captures different meanings at once
- Handles long-range dependencies
- improves model accuracy
- Enables parallel computation
Limitations:
- Computationally expensive
- Requires more memory
- Harder to interpret individual heads
Real-World Applications:
Multi-Head Attention is used in:
● Machine translation
● Chatbots (ChatGPT)
● Text summarization
● Question answering
● Image and speech models

Simple Exam Answer (Long):
Multi-Head Attention is a mechanism used in Transformer models where
multiple attention heads operate in parallel to focus on different parts of the
input sequence. Each head captures different relationships between words,
and their outputs are combined to produce a richer and more accurate
representation of the text.
Role of Multi-Head Attention in Encoder and
Decoder:
Encoder:
● Uses multi-head self-attention
● Each word attends to all other words in the sentence
Decoder:
Uses two types:
1.Masked multi-head self-attention:
○ Prevents seeing future words
2.Encoder-decoder attention:
○ Focuses on relevant input words.
This combination enables accurate text generation.
Masked Multi-Head Attention (Easy Explanation):
Masked attention hides future words during decoding.
Sentence:
“I am learning transformers”
When predicting “learning”, the model can only see:
● I
● am
Not:
● transformers
This ensures causal behavior in language generation.
Conclusion:
Multi-Head Attention allows AI models to understand language deeply by viewing sentences from multiple perspectives at the same time. This powerful idea is a key reason why Transformer-based models outperform traditional NLP systems.