Overfitting Introduction:
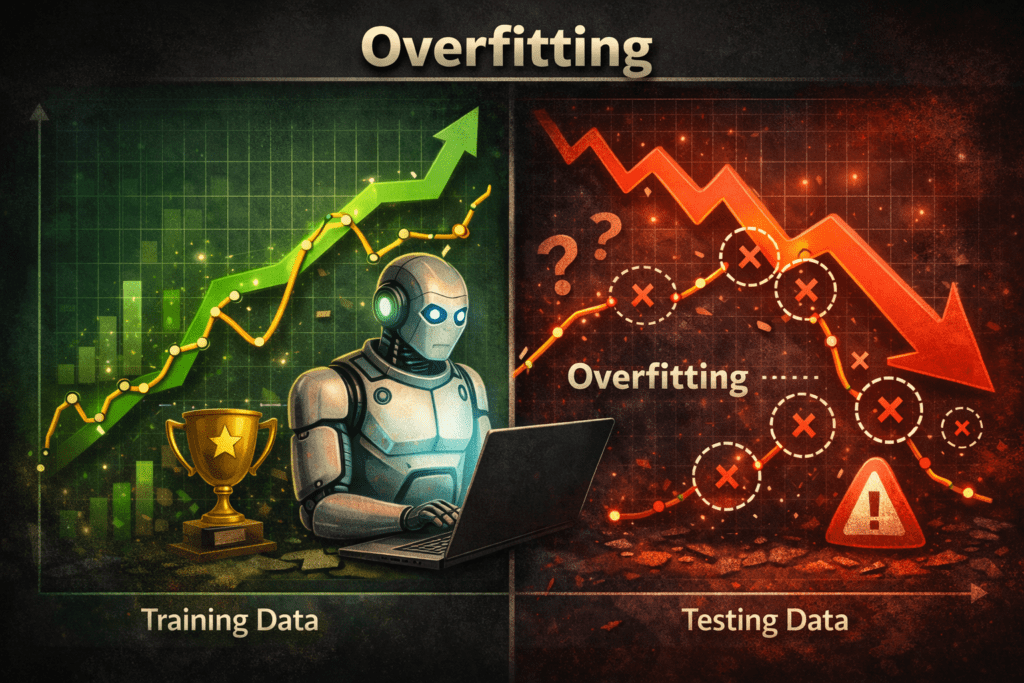
Overfitting is a common problem in machine learning where a model learns the training data too well, including its noise and unnecessary details, and therefore performs poorly on new, unseen data.
Overfitting is a common problem in machine learning that occurs when a model learns the training data too thoroughly, including its noise and minor details. Instead of capturing the underlying patterns that generalize well to new data, the model memorizes the training examples. As a result, it achieves very high accuracy on the training dataset but performs poorly on unseen or testing data. Overfitting reduces the model’s ability to generalize and makes it unreliable for real-world applications.
Simple Definition:
Overfitting occurs when a machine learning model performs very well on training data but poorly on test or real-world data.
Overfitting is a condition in machine learning where a model learns the training data too well, including noise and small details, which reduces its ability to perform well on new, unseen data.
Imagine a student who:
● memorizes all answers from a textbook.
● scores full marks in practice tests.
● fails when questions are asked differently in the exam.
Example:
Suppose we train a model to predict house prices.
● Training Data: Perfect predictions.
● New Houses: Very wrong predictions.
This means the model:
● learned specific patterns.
● failed to learn general rules.
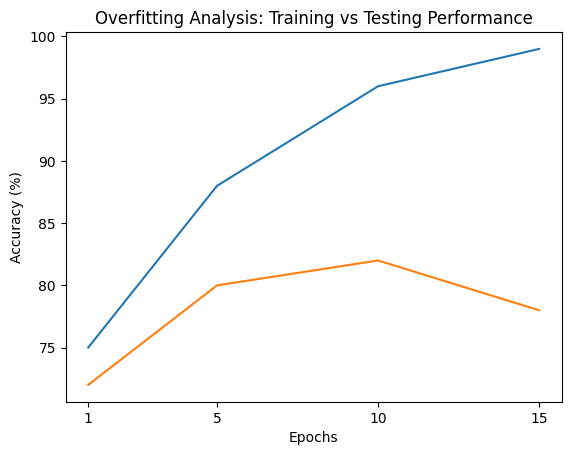
Training vs Testing Performance:
| Model / Epoch | Training Accuracy (%) | Testing Accuracy (%) | Training Loss | Testing Loss | Observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch 1 | 75% | 72% | 0.65 | 0.70 | Good learning, balanced performance |
| Epoch 5 | 88% | 80% | 0.35 | 0.50 | Slight gap between train & test |
| Epoch 10 | 96% | 82% | 0.10 | 0.55 | Overfitting starts |
| Epoch 15 | 99% | 78% | 0.02 | 0.75 | Clear overfitting |
Training Data 98%.
Testing Data 65%.
Why Overfitting Happens:
1️.Model Too Complex:
● Too many layers.
● Too many parameters.
● Deep trees.
2️.Small Training Dataset:
● Not enough examples.
● Model memorizes samples.
3️.No Regularization:
● No constraints on learning.
4️.Too Many Training Epochs:
● Model trains too long.
How to Detect Overfitting:
● High training accuracy.
● Low validation/test accuracy.
● Validation loss starts increasing.
● Large gap between train & test curves.
How to Prevent Overfitting:
1. Use More Data:
More data = better generalization.
2. Regularization:
L1 (Lasso).
L2 (Ridge).
Dropout (Neural Networks).
3. Early Stopping:
Stop training when validation loss increases.
4. Data Augmentation:
Create more variations of data.
5. Simpler Models:
Reduce layers or parameters.
Overfitting vs Underfitting:
Simple Difference in One Line:
- Overfitting: High training accuracy, low testing accuracy.
- Underfitting: Low training accuracy, low testing accuracy.
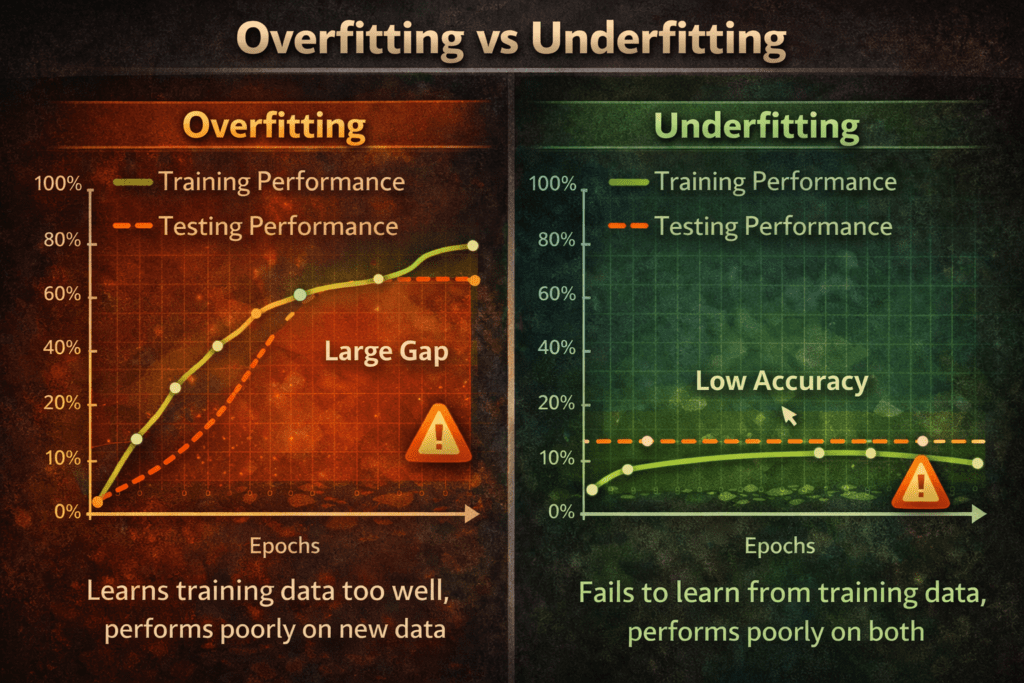
Feature Overfitting Underfitting:
- Training Accuracy Very High Low.
- Test Accuracy Low Low.
- Model Complexity Too High Too Low.
- Bias Low High.
- Variance High Low.
Overfitting in Deep Learning:
Overfitting in deep learning occurs when a neural network learns the training data too precisely, including its noise and minor details, instead of capturing the underlying patterns that generalize well to new data. Deep learning models, such as deep neural networks, typically contain a large number of parameters, which makes them highly powerful but also more prone to overfitting. When overfitting happens, the model achieves very high accuracy on the training dataset but performs poorly on validation or test data.
Why Deep Learning Models Overfit Easily?
Overfitting is a common problem in machine learning where a model performs extremely well on training data but poorly on new, unseen data. It happens when the model learns not only the underlying patterns but also the noise and random fluctuations present in the training dataset. As a result, the model fails to generalize effectively to real-world scenarios.
1️.Large Number of Parameters:
● many layers.
● millions (or billions) of weights.
This gives them high learning capacity, making memorization easy.
2️.Limited Training Data:
Deep models require huge datasets.
When data is limited:
● the model remembers examples.
● generalization fails.
3️.Long Training Time:
Training for too many epochs causes the model to:
● fit noise.
● lose general patterns.
4️.Lack of Regularization:
Without constraints:
● weights grow large.
● model becomes overly complex.
Overfitting in Machine Learning:
Overfitting is one of the most common challenges in machine learning. It occurs when a model learns the training data too well, capturing not only the underlying patterns but also the noise and minor fluctuations. As a result, the model performs exceptionally well on training data but fails to generalize to new, unseen data. This reduces its reliability in real-world applications.
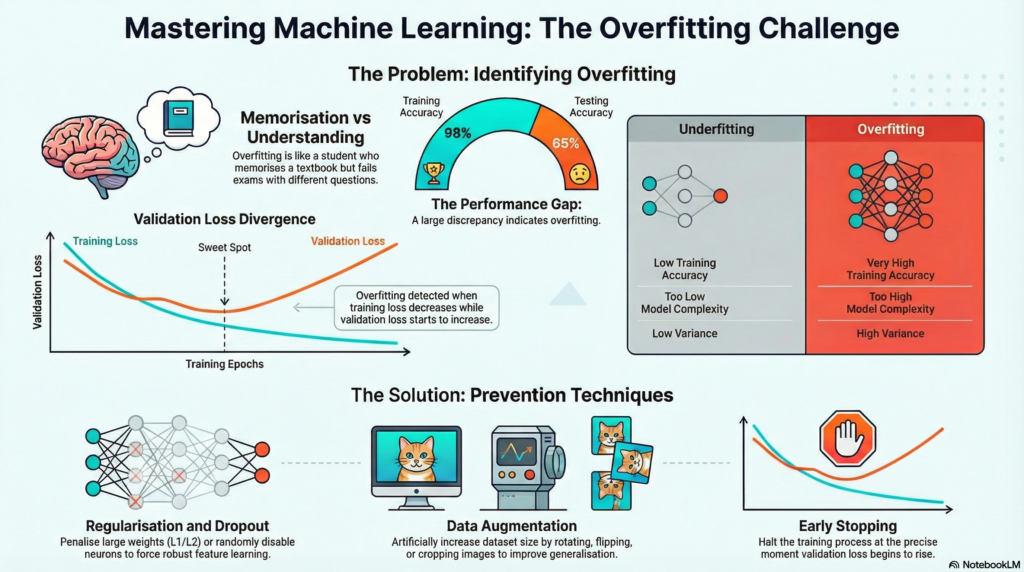
Techniques to Prevent Overfitting in Deep Learning:
1. Dropout
● Randomly disables neurons during training.
● Forces network to learn robust features.
Example:
Dropout rate = 0.5.
2. Data Augmentation
Artificially increase dataset size:
● rotate images.
● flip images.
● add noise.
● crop images.
Helps the model see varied data.
3. Early Stopping
Stop training when:
● validation loss starts increasing Prevents learning noise.
4. Regularization (L1 & L2)
Adds penalty to large weights:
● L1 → sparsity.
● L2 → smooth weights.
Overfitting in Modern Deep Models:
Even large models like:
● CNNs.
● RNNs.
● Transformers.
Use:
● dropout.
● layer normalization.
● massive datasets.
to control overfitting.
Key Takeaways:
● Deep learning models overfit easily due to high capacity.
● Large datasets and regularization are essential.
● Monitoring validation loss is critical.
● Proper techniques improve generalization.
Conclusion:
Overfitting is a critical issue in machine learning that limits a model’s ability to generalize beyond its training data. While achieving high training accuracy may seem impressive, the true goal of machine learning is to build models that perform well on unseen data. By carefully monitoring performance and applying proper regularization techniques, overfitting can be effectively controlled.