Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern it’s a business survival strategy. As we move toward 2026, organizations face an increasingly complex threat landscape shaped by artificial intelligence, cloud-native infrastructure, remote work, regulatory pressure, and a growing shortage of skilled security professionals.
This article lays out a practical cybersecurity roadmap to 2026 one that works for enterprises, SMBs, and even individuals entering the field. Whether you’re a business leader, IT manager, or aspiring professional, this guide will help you understand what to prioritize, when to invest, and how to prepare.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy a Cybersecurity Roadmap Is Critical in 2026
A cybersecurity roadmap is a strategic, multi-year plan that aligns security initiatives with business goals, risk tolerance, and future threats. By 2026, organizations without a clear roadmap will face:
- Increased ransomware and AI-driven attacks
- Regulatory penalties and compliance failures
- Brand damage from data breaches
- Operational downtime and financial loss
Cybersecurity can no longer be reactive. Firewalls and antivirus tools alone won’t cut it. Organizations must plan holistically, balancing people, processes, and technology.
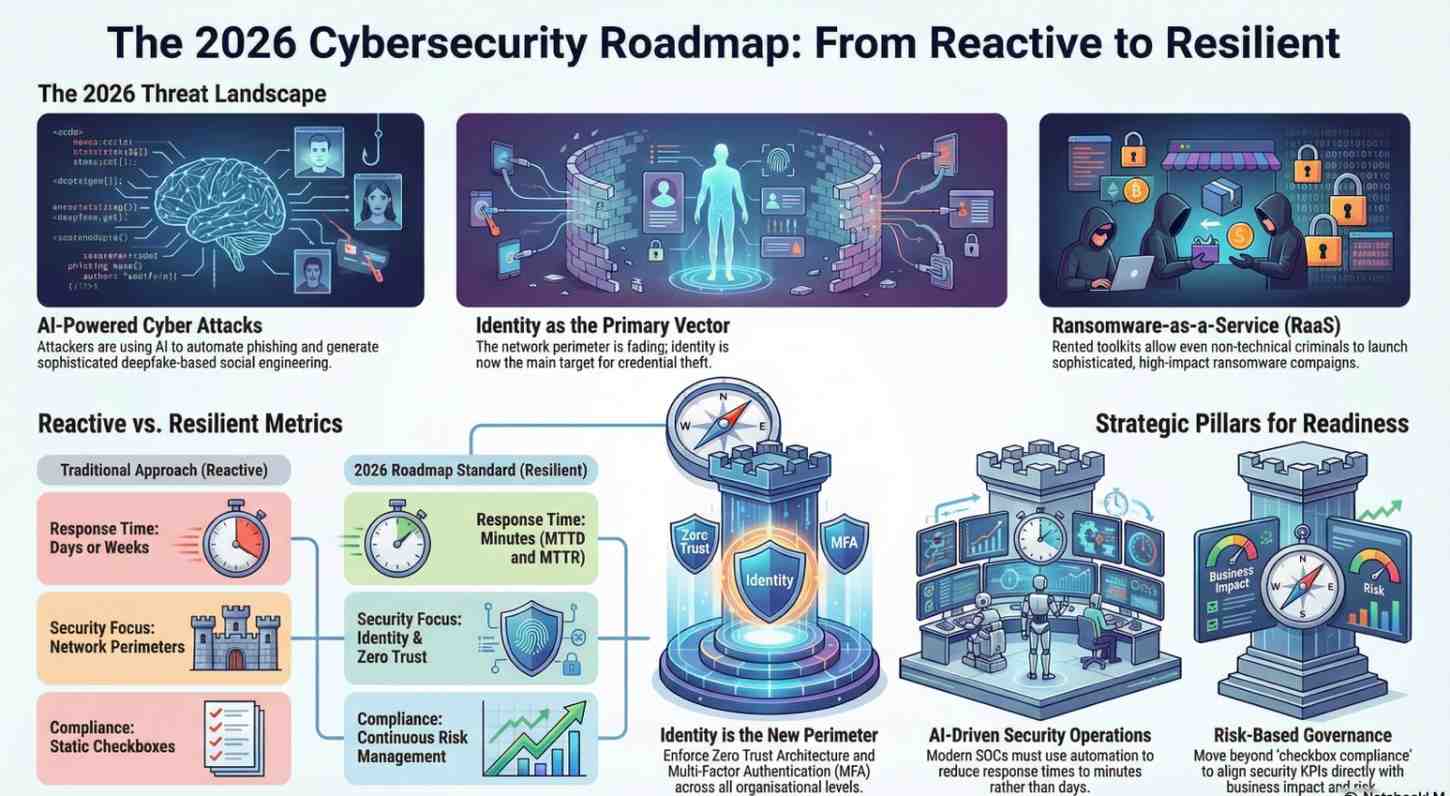
The Cyber Threat Landscape Heading Into 2026
1. AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
Attackers are now using AI to:
- Automate phishing campaigns
- Generate deepfake-based social engineering
- Rapidly discover vulnerabilities
Defenders must match this pace with AI-driven detection and response.
2. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Ransomware has evolved into a business model. Even non-technical criminals can launch sophisticated attacks using rented toolkits.
3. Cloud and Supply Chain Risks
As organizations rely on:
- SaaS platforms
- Cloud providers
- Third-party vendors
The attack surface expands, and trust assumptions become dangerous.
4. Identity-Centric Attacks
By 2026, identity not the network perimeter will be the primary attack vector.
Core Pillars of the Cybersecurity Roadmap to 2026
Every effective cybersecurity roadmap is built on five foundational pillars:
- Governance & Risk Management
- Identity & Access Management
- Security Architecture & Technology
- Security Operations & Incident Response
- People, Skills & Culture
Let’s break these down.
Pillar 1: Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC)
What Changes by 2026
- Stricter global data protection laws
- Increased board-level accountability
- Mandatory breach disclosure timelines
Roadmap Priorities
- Establish a risk-based security strategy
- Move beyond checkbox compliance
- Align cybersecurity KPIs with business impact
- Regular threat modeling and risk assessments
Key Outcome
Security becomes a business enabler, not a cost center.
Pillar 2: Identity Is the New Perimeter
Why Identity Dominates the 2026 Roadmap
Most breaches now start with:
- Stolen credentials
- Weak passwords
- Over-privileged accounts
Roadmap Actions
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) everywhere
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture
- Use least-privilege access models
- Monitor identity behavior continuously
Tools to Prioritize
- IAM (Identity & Access Management)
- PAM (Privileged Access Management)
- Continuous authentication
Pillar 3: Security Architecture & Technology Evolution
Cloud-Native Security by Default
By 2026, organizations must secure:
- Multi-cloud environments
- Containers and Kubernetes
- Serverless workloads
Technology Focus Areas
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR/XDR)
- Post-quantum cryptography preparation
Roadmap Tip
Avoid tool sprawl. Integration matters more than tool count.
Pillar 4: Security Operations & Incident Response
The SOC of 2026
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) will be:
- Highly automated
- AI-assisted
- Focused on response, not alerts
Key Roadmap Investments
- SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response)
- Threat intelligence platforms
- Continuous exposure management
- Tabletop incident response exercises
Success Metric
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) measured in minutes, not days.
Pillar 5: People, Skills & Cyber Culture
Technology alone won’t save you.
Human Risk Is the Biggest Risk
Employees remain the #1 attack vector through:
- Phishing
- Social engineering
- Misconfigurations
Roadmap Actions
- Continuous security awareness training
- Role-based training (not generic videos)
- Leadership-level cyber education
Cybersecurity Roadmap for Beginners
If you’re new to cybersecurity whether as a student, career switcher, or business owner this simplified roadmap helps you get started.
Phase 1: Foundations
- Networking basics (TCP/IP, DNS, HTTP)
- Operating systems (Linux & Windows)
- Security fundamentals (CIA triad)
Phase 2: Core Skills
- Basic scripting (Python, Bash)
- Understanding common attacks (phishing, malware, SQL injection)
- Intro to cloud security
Phase 3: Tools & Practice
- Firewalls and SIEM basics
- Vulnerability scanning
- Hands-on labs and simulations
This cybersecurity roadmap for beginners builds the foundation needed to specialize later.
Cybersecurity Engineer Roadmap to 2026
For aspiring or current professionals, the cybersecurity engineer roadmap is becoming more specialized and strategic.
Core Technical Skills
- Network & cloud security
- Endpoint protection
- Identity and access management
- Secure architecture design
Advanced Skills by 2026
- AI-driven security analytics
- Threat hunting
- Zero Trust implementation
- Secure DevOps (DevSecOps)
Soft Skills That Matter
- Risk communication
- Business alignment
- Incident leadership
- Documentation and reporting
Cybersecurity engineers in 2026 won’t just “fix alerts” they’ll design resilient systems.
Aligning Business Goals With the Cybersecurity Roadmap
A successful roadmap must answer:
- What risks matter most to the business?
- What assets are mission-critical?
- What level of risk is acceptable?
Roadmap Alignment Checklist
- Executive sponsorship
- Clear metrics and milestones
- Budget planning over multiple years
- Regular roadmap reviews
Common Mistakes Organizations Make
Avoid these roadmap killers:
- Buying tools without strategy
- Treating compliance as security
- Ignoring identity security
- Underinvesting in people
- No incident response planning
Measuring Progress Toward 2026
Key metrics to track:
- Security maturity level
- Incident response time
- Percentage of automated responses
- Employee phishing resilience
- Third-party risk exposure
Final Thoughts: Security as a Journey, Not a Destination
The cybersecurity roadmap to 2026 is not a static document it’s a living strategy. Threats will evolve. Technology will change. Regulations will tighten. The organizations that succeed will be those that adapt continuously.
Whether you’re:
- A business leader planning long-term security
- A beginner exploring cybersecurity
- Or a professional following a cybersecurity engineer roadmap
The time to act is now.
Cybersecurity in 2026 won’t reward those who react it will reward those who prepare.
- Explore CyberSecurity basics here, then master it with Jeevi’s resources and our complete CyberSecurity training.





