Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction :
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence has taken a giant leap forward in understanding
and generating human language. At the center of this revolution is a powerful model design
known as the Transformer Architecture. From chatbots like ChatGPT to translation tools and
search engines, transformers are the engine driving today’s smartest AI systems.
What Is Transformer Architecture:
The Transformer Architecture is a deep learning framework designed to process
sequential data such as text. Unlike traditional models that read data step by step, transformers
analyze the entire input sequence at once. This allows them to understand context,
relationships, and meaning more effectively.
The transformer was introduced in the research paper “Attention Is All You Need”, which
replaced older sequence-based approaches with attention-based learning.
Why Transformer Architecture Was Introduced:
Earlier models like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term
Memory (LSTM) networks had limitations:
● They processed words sequentially, making training slow
● They struggled with long-range dependencies
● Important context could be lost over time
Transformers solved these problems by removing recurrence and using attention mechanisms instead.
Core Components of Transformer Architecture:
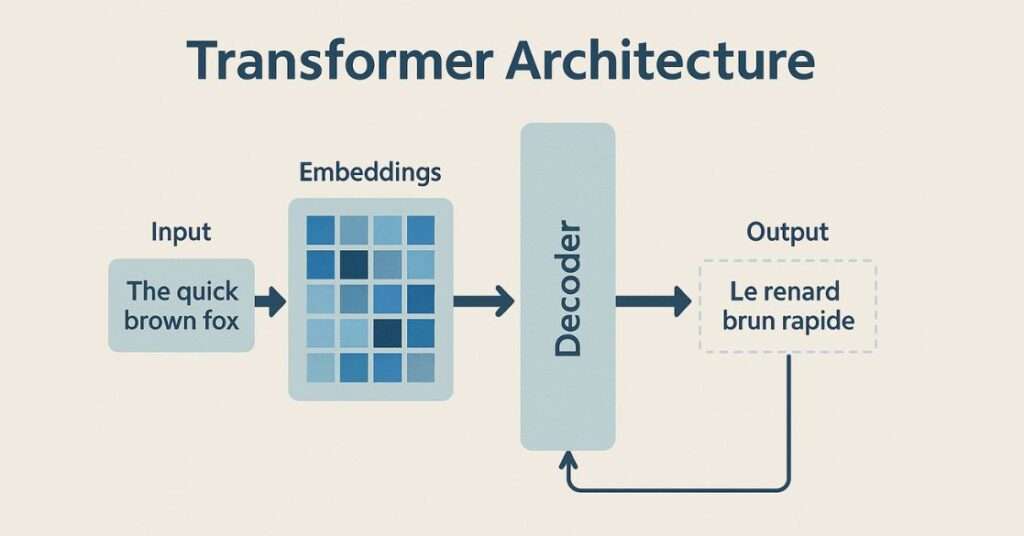
Word Embeddings:
Input words are converted into numerical vectors that represent their meaning in a mathematical
form.
Positional Encoding:
Since transformers do not process words in order, positional encoding is added to help the
model understand the sequence and position of each word.
Self-Attention Mechanism:
Self-attention allows each word to focus on other relevant words in the sentence. This helps the
model understand context and relationships between words, even if they are far apart.
Encoder and Decoders:
● Encoder: Reads and understands the input text
● Decoder: Generates output text based on the encoded information
Some models use only encoders (BERT), while others use only decoders (GPT).
Feed-Forward Neural Networks:
These layers further process the information received from the attention mechanism to refine
understanding.
Residual Connections and Layer Normalization:
These techniques help stabilize training and improve performance in deep networks.
How Transformer Architecture Works:
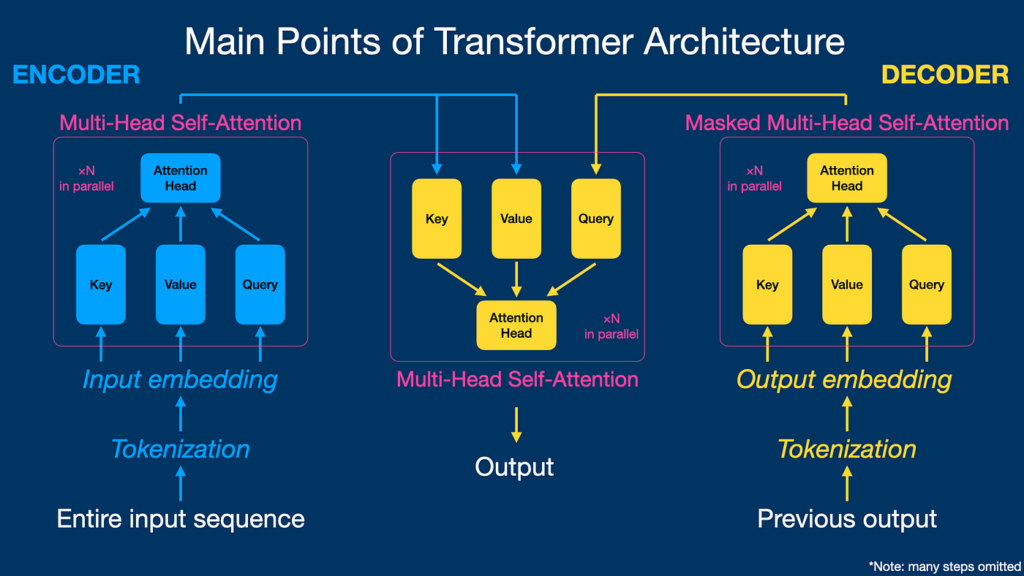
- Input text is converted into embeddings
- Positional information is added
- Self-attention finds relationships between all words
- Encoders extract deep meaning
- Decoders generate the final output
All these steps happen in parallel, making transformers faster and more efficient.
Advantages of Transformer Architecture:
● Parallel Processing – Faster training and inference
● Strong Context Understanding – Handles long sentences well
● Scalability – Performs better with large datasets
● Versatility – Used beyond text, including vision and speech
Applications of Transformer Architecture
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Transformers have transformed NLP tasks by enabling models to understand context,
semantics, and relationships in text.
Key Applications in NLP:
a) Language Translation:
● Models: Google Translate, MarianMT
● Transformers replace RNNs/LSTMs for faster, more accurate translation
● Handles long sentences and complex grammar
● Example: Translating English → French or Japanese → English
b) Text Summarization:
● Models: BART, T5
● Converts long documents into concise summaries
● Widely used for news summarization, research papers, legal documents.
c) Question Answering (QA):
● Models: BERT, RoBERTa
● Understands context in passages to answer questions
● Used in search engines and virtual assistants
d) Sentiment Analysis:
● Models: DistilBERT, XLNet
● Determines sentiment (positive, negative, neutral) in text
● Applied in social media monitoring and customer feedback analysis
e) Text Generation:
● Models: GPT series, OPT, LLaMA
● Generates coherent and contextually relevant text
● Used in chatbots, AI writing assistants, and content creation
Speech and Audio Processing:
Transformers are increasingly used in audio tasks due to their ability to model long-range
dependencies.
Applications:
a) Speech Recognition:
● Model: Wav2Vec 2.0
● Converts spoken language into text
● Used in virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa
b) Text-to-Speech (TTS)
● Models: Tacotron 2, FastSpeech
● Converts text into natural-sounding audio
● Used in audiobooks, navigation systems, and accessibility tools
c) Audio Classification:
● Detect emotions, speaker identification, or music genres
● Used in call centers and music streaming app
3.Computer Vision:
Transformers have also entered the visual domain with Vision Transformers (ViT).
Applications:
a) Image Classification:
● Model: Vision Transformer (ViT)
● Classifies images into categories with high accuracy
● Used in medical imaging, autonomous vehicles, and facial recognition
b) Object Detection:
● Model: DETR (DEtection TRansformer)
● Detects and localizes multiple objects in images
● Applied in surveillance, robotics, and self-driving cars
c) Image Generation:
● Model: DALL·E, Imagen
● Generates images from textual descriptions
● Used in creative industries, design, and AI art
Multimodal AI:
Transformers excel in integrating multiple types of data, such as text, images, and audio.
Examples:
● CLIP (OpenAI): Understands images and text simultaneously
○ Enables image search using natural language
● Flamingo (DeepMind): Performs tasks with both images and text
● Applications: AI-assisted content creation, image captioning, multimodal search engines
Recommendation Systems:
Transformers capture user-item interactions effectively, outperforming traditional collaborative
filtering models.
Applications:
● Video recommendations (YouTube, Netflix)
● E-commerce product suggestions (Amazon)
● Personalized content feeds (TikTok, Instagram)
Code Generation and Programming:
Transformers trained on code can understand and generate programming scripts.
Applications:
● GitHub Copilot, CodeT5, Codex
● Auto-completes code, generates functions, or translates code between languages
● Speeds up software development and debugging
Scientific Research and Drug Discovery:
Transformers can model molecular structures, proteins, and chemical interactions.
Applications:
● Protein folding prediction (AlphaFold)
● Drug-target interaction prediction
● Chemical property prediction
● Accelerates research in biotechnology and chemistry
Time Series and Forecasting:
Transformers can process sequential data faster and more effectively than RNNs.
Applications:
● Stock market prediction
● Weather forecasting
● Energy demand prediction
● Anomaly detection in industrial processes
Reinforcement Learning:
Transformers are used as sequence models for decision-making tasks.
Applications:
● Game AI (AlphaStar)
● Robotics control
● Planning and optimization tasks
Advantages of Transformers in Applications:
- Parallelization – Faster training compared to RNNs
- Long-range context – Captures dependencies over long sequences
- Scalability – Works with billions of parameters for LLMs
- Versatility – Handles text, audio, images, and multimodal data
- State-of-the-art performance – Achieves top results across domain
Limitations:
● Requires large datasets and compute resources
● May generate biased outputs if trained on biased data
● Memory-intensive for very long sequences
Key Takeaway:
The Transformer architecture is a versatile, powerful model capable of
handling text, speech, images, code, and multimodal data. Its self-attention
mechanism, scalability, and parallelization make it the foundation of modern
AI applications across industries.
Transformers used in:
- Machine Translation
- Chat box and conversational AI
- Text Summerization
- Search Engine
- Speech Recognition
Conclusion:
The transformer architecture is a milestone in artificial intelligent. By replacing sequential processing with attention – based learning, it allows machines to understand context. meaning, and relationships at scale.