In this blog post, we will talk about what a DevOps engineer does in the IT industry. A DevOps engineer is a role that is in high demand these days and for good reason. As the world becomes more and more digital, it is important that everything runs smoothly. That includes the systems that our businesses use. So if you are looking for a career change or want to learn more about this growing field, be sure to check out this blog post.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is DevOps?
DevOps is a software development and delivery process that aims to increase collaboration between engineering teams and Operations staff so that the systems being developed are delivered quickly, efficiently, and with high quality. DevOps was originally created in response to the challenges of building critically needed web applications in an era where infrastructure changes rapidly.
The goal of DevOps is twofold: improve overall system reliability through automated tooling and processes, while also freeing up engineers to work on higher-value projects. In essence, we want our developers to be more “autonomous” while still relying on a tightly coordinated Operations team to keep the systems running.
1. Day-to-Day Operations
A DevOps engineer is responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations of software development or IT environment. They work with developers, operators, and other members of an organization to ensure that applications are deployed, monitored, and scaled as needed.
DevOps engineers will work with various stakeholders to understand the needs of the organization and develop a plan that meets those needs. They will also be responsible for making sure all systems are integrated into an overall DevOps Culture.
DevOps engineer will also work closely with the Project Manager and other team members to define the requirements of a project, monitor the progress of the project closely, and take corrective action as needed.
Additionally, they may be involved in creating and maintaining automation tools to help with this process. They also work closely with customers or clients to ensure that their needs are being addressed and that the software is running as smoothly as possible.
In the day-to-day task, the DevOps engineer will use CICD Pipeline, Version Control systems such as Git or Gitlab, Deployment tools such as Puppet or Chef, Monitoring tools such as dynatrace, datadog, and Scalability solutions like Kubernetes or Docker.
If their IT company is matured in Cloud adoption, they may be using some of the Cloud Providers such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. If they do so, they may need to work on Cloud Native solutions as well.
2. Automating Infrastructure
DevOps engineers often work to automate the deployment and management of IT systems. This can involve developing scripts or tools that make tasks such as scaling, deploying, and monitoring easier for organizations.
Some common automation task done by DevOps engineers include:
- Scripts to automate the installation and configuration of software packages
- Tooling to monitor system performance and health
- Scripts to detect and diagnose problems with systems
- Establish or Integrate CICD pipeline with various cloud-native tools
- Monitoring tools to track system performance
- Tools to check for software updates and patches
- Tools to detect problems with systems
- Setup Infrastructure using Terraform, Cloudformation, Pulumi, or Ansible
- Building and Packaging the Software
- Database backups and upgrades
- Regression test and Code Scanning
- Package deployment
- Trigger builds when code is modified by the developer.
Additionally, Setting up an Infrastructure pipeline to automate the provision of cloud resources such as EC2, Lambda, Dynamodb, Redshift, Kubernetes and Docker, and many more.
The benefits of Automation include faster deployment times, improved system efficiencies, and increased safety.
Finally, You can automate a large portion of the DevOps lifecycle using both Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) practices.
3. Establishing Standards
DevOps engineers are responsible for establishing standards across an organization’s software development or IT environment. They may work with other departments to develop best practices or develop standardized methods for performing certain tasks.
DevOps standards may include:
- Creating and enforcing application release schedules
- Configuring systems to use common software configurations
- Developing or adopting standardized coding and development practices
- Follow the environmental baseline.
- Establish Build, Run, and Test Methods
- Creating an ideal DevOps Culture
Moreover, DevOps engineers are responsible for ensuring that all software development or IT operations take place under a DevOps culture. This may include:
- Ensuring that teams use common tools and techniques
- Encouraging code collaboration and sharing
- Identifying and resolving conflicts through coordinated work
- Offering feedback and recognition to team members
4. Configuring and Operating Systems
DevOps engineers are often responsible for configuring and operating systems. This may include setting up servers, deploying applications, and monitoring systems. They also may work to improve the performance of these systems by tweaking configurations or installing new software.
DevOps engineer often works on Public cloud and Private Cloud infrastructure. Hence, the DevOps engineer needs to configure the operating system to run on both environments.
5. Lifecycle Management
DevOps engineers are often responsible for managing software development and IT environments throughout their entire lifespan. This may include planning and implementing upgrades, organizing workflows, and orchestrating communication between members of an organization.
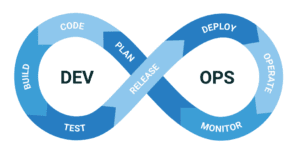
If you talk about the DevOps lifecycle, There are 10 phases in the development lifecycle which include:
- Plan
- Code
- Build
- Test
- Package
- Release
- Deploy
- Operate
- Monitor and Finally Repeat!
which is basically doing the same thing over and over again to produce a product or service that meets the customer’s needs.
Moreover, in order to manage software development and IT environments effectively, DevOps engineers often need to have strong coordination and communication skills. They must be able to work with different teams throughout an organization and understand their goals in order to successfully coordinate efforts.
In conclusion, DevOps engineers are responsible for a wide range of tasks that can include setting up and operating systems, managing software development and IT environments, and coordinating efforts between different teams. They need to have strong coordination and communication skills in order to successfully manage these complex projects.






